Microsoft Platform (Range 7.0.0.x)
Available soon.
About
The Microsoft Platform connector enables the monitoring of servers that run the Microsoft Windows OS. Leveraging Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), it provides visibility on system performance, health metrics, and operational status.
To query data from the monitored server, the connector uses Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) extensions.
All versions of Microsoft Windows are supported, as long as the connector is able to retrieve data using WMI.
Important
Currently, ranges 1.1.3.x and 6.0.0.x are still supported. However, we strongly recommend switching to range 7.0.0.x as soon as it is available.
Configuration
Connections
Virtual Connection
This connector uses a virtual connection and does not require any input during element creation. However, once the element is created, it is necessary to configure the connection settings (available in the page General -> Connections).
In addition, WMI and DCOM must be properly configured on the server to be monitored, as detailed below.
Important
Since this is a virtual connector, WMI queries sent to the target server are not displayed in the Stream Viewer
WMI configuration
- To go to WMI Control Properties, go to Start > Run and enter wmimgmt.msc.
- Right-click WMI Control (Local) and select Properties.
- On the Security tab page, go to \Root\CIMV2 and click the Security button.
- Add the user that will be used to query data from the remote server to the list and give the user all rights.
- Apply all.
DCOM configuration
- Go to Start > Run and enter dcomcnfg (Component Services).
- Under Component Services > Computers, right-click My Computer and select Properties.
- Go to the tab COM Security.
- Under Launch and Activation Permissions, click Edit Limits.
- Add the user and give the user the Local Launch, Remote Launch, and Remote Activation permissions.
- Apply all.
Note
- After DCOM settings have been changed, the WMI services sometimes need to be restarted.
- This method works fine for a Windows XP system but cannot be used on a Windows Server 2003 SP1.
- On a Win2K3, the local user must be added to the administrators group.
- On a Win2K8, the local user must be added to the administrators group, Distributed COM Users, and Performance Monitor Users.
Polling Frequencies
Currently the polling frequencies are hard-coded in the connector. Below you can find a summary of the polling frequencies per metric group.
Fast Timer (10 seconds):
- CPU Utilization
- Memory
- Process Instances
- Process Instance Details
- Processes
Medium Timer (1 minute):
- CPU Metrics
- Disk Details
- Network Adapters
- Network Adapter Details
Slow Timer (1 hour)
- System
- Operating System
- Operating System Updates
- CPU Info
Timeout Settings
- Default timeout for a single command: 1.5 seconds
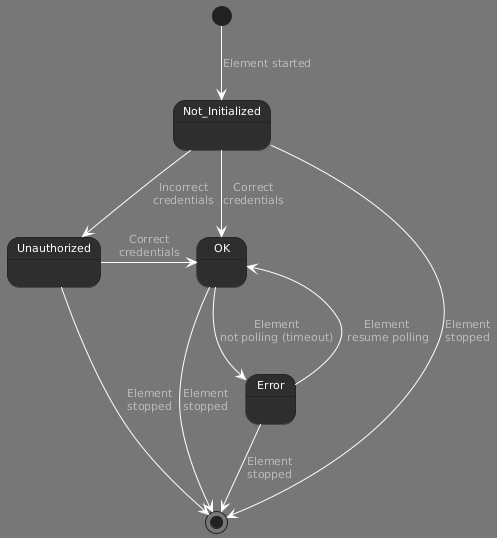
Connection States
How to use
The General page provides details about the operating system running on the monitored server, while the OS Updates page displays details about the recently installed patches on the server.
The CPU page offers information related to the processor, including usage metrics, as well as thread and handle counters, and the Logical Processors page presents utilization metrics for each logical processor.
The Memory page provides information about the physical and virtual memory allocation of the monitored server.
The Disk page offers information about the local storage in the monitored server. Further information, such as rates, and read, write and transfer times, is available on the Disk Details page.
Note
A sign that could indicate that the disk is busy is the Latency, i.e. how long it takes before it can process something. This metric can be tracked with the parameter Avg. Transfer Rate.
The Network page contains information about the network adapters available in the monitored server. Additional metrics, such as rates, are available on the Details subpage.
Note
By default, the column Name will contain the name of the adapter as retrieved by WMI. However, in some cases, the connector may not be able to retrieve the name.
The Process page lists all the current processes run by the monitored server (similar to the Task Manager tool available in any Microsoft Windows OS). The connector will remove any process from the table that is no longer running in the monitored server. This page has two subpages:
Process Details: Provides counters and rates for the current processes run by the monitored server.
Process Overview: This page display the Processes table, which can be used for the following purposes:
- Monitoring processes that are no longer running on the monitored server. By default, this table is empty. You can right-click in the table to add or remove specific processes via the context menu. If a process is not running on the monitored server, the column Count will be set to 0.
- Monitoring multiple instances of the same process. For example, if you would like to monitor all the instances of the Microsoft Edge browser, you can add the process msedge.exe.
Note
- The process you add does not need to be running in the operating system. Make sure that you use the exact process name, including the extension.
- You can also add an existing process to the table Processes by right-clicking a process in the Process Instances table and selecting the option Validate process.
- Wildcards are currently not supported.
The Services page provides information about the services available on the monitored server.
The Service Validation page allows you to track if services are still available in the monitored server. By default, this table is empty.You can right-click in the table to add or remove specific services via the context menu.
Note
You can also add an existing service to the Service Validation table by right-clicking a service in the Services table and selecting the option Validate service. Multiple services can be added this way.
The Software page displays the list of installed applications on the monitored server.
Notes
For a list of the WMI queries implemented in the connector, refer to Microsoft Platform - WMI Queries.
In case the element is not able to poll the monitored server, please follow the Troubleshooting guide.