Troubleshooting
Merge conflicts
Scenario 1: web editor
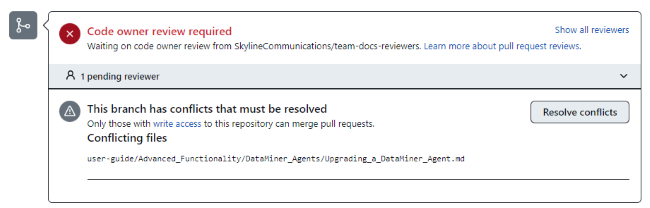
Symptom: After you create a pull request, you see a warning that the branch contains conflicts that must be resolved before your branch can be merged into the main branch.
Resolution:
If the Resolve conflicts button is deactivated, your pull request's merge conflicts are too complex to resolve in the web editor. In this case, use GitHub Desktop and Visual Studio Code to resolve the conflicts.
If you can click the Resolve conflicts button, proceed to resolve the merge conflicts in the web editor.
On the left side of the web editor, a list of conflicting files is displayed. The header bar shows the number of conflicts in the current file.

To resolve the merge conflict(s):
Decide whether to keep your branch's changes (i.e. the current changes), the main branch's changes (i.e. the incoming changes), or combine both. The bracket on the left indicates the beginning and end of the current and incoming changes.
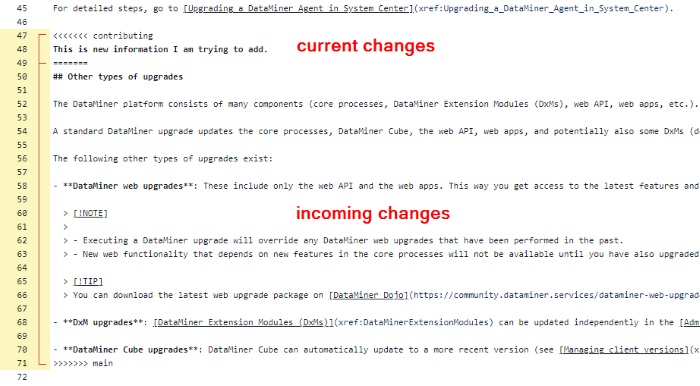
Delete the conflict markers
<<<<<<<,=======, and>>>>>>>.If multiple merge conflicts exist in the file, scroll down to the next set of conflict markers, and repeat the previous steps to resolve your merge conflict.
Click Mark as resolved in the top-right corner of the header bar.
If multiple files have conflicts, select the next file you want to edit and repeat the previous steps until all merge conflicts are resolved.
To save your changes, select Commit merge.
Scenario 2: GitHub Desktop
Symptom:
You encounter one of the following situations:
After you create a pull request, you see a warning that the branch contains conflicts that must be resolved before your branch can be merged into the main branch. However, your pull request's merge conflicts are too complex to resolve in the web editor.
In GitHub Desktop, when you try to merge the main branch into your current branch, you get a warning that there are one or multiple conflicted files.
Note
If this is your starting point, skip directly to the Open in Visual Studio Code step in the procedure below.
Resolution:
Note
Ensure you have Visual Studio Code installed before following this procedure.
In GitHub Desktop, make sure the branch containing your changes is selected.
Select Current branch > Choose a branch to merge into [name-of-your-branch].
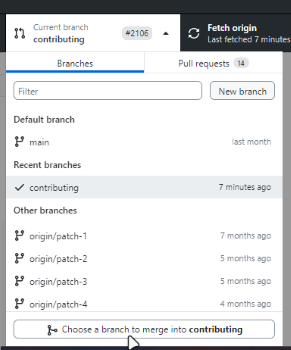
Select to merge the main branch into your branch.
A warning will appear indicating conflicted files.
Click Create a merge commit.
Note
Make sure the main branch is up to date. If you suspect the latest changes are not on your local machine, switch to the main branch, and click Fetch origin to receive the latest changes from the remote repository. Then switch back to the branch containing your changes.
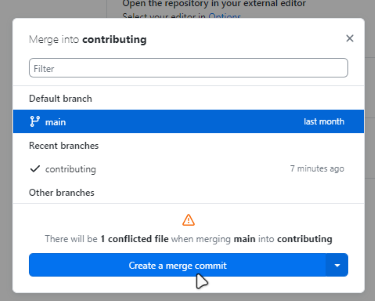
GitHub Desktop will display a list of merge conflicts to be resolved.
Select Open in Visual Studio Code.
If there are several files with merge conflicts, this button is available for each file. Use the button for one of the files. When you have resolved the conflicts in that file as detailed below, you can then continue with the next one.
In Visual Studio Code, decide whether you want to keep your branch's changes (i.e. the current changes), the main branch's changes (i.e. the incoming changes), or if you want to combine the two.
Color indicators represent the beginning and end of the current and incoming changes.
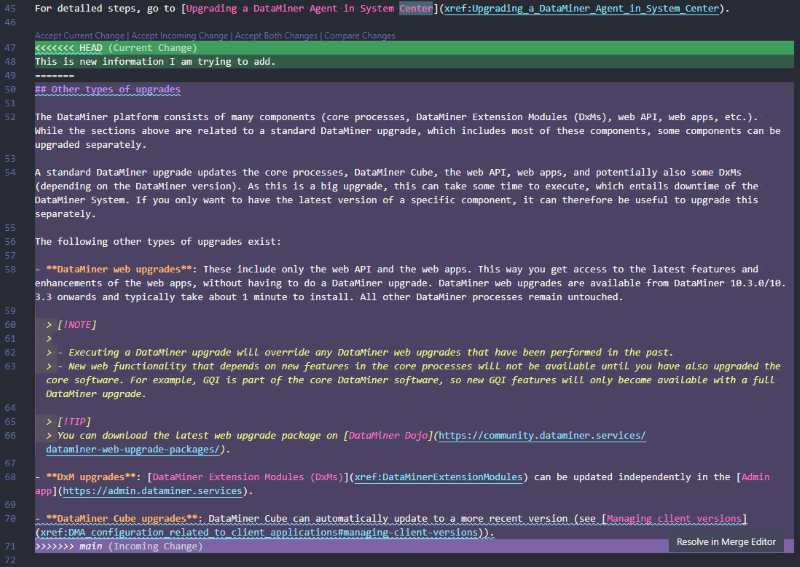
Either select a preset option, e.g. Accept Incoming Change, or resolve the conflict manually and delete the conflict markers
<<<<<<<,=======, and>>>>>>>.If multiple merge conflicts exist in the file, scroll down to the next set of conflict markers, and repeat the two previous steps to resolve your merge conflict.
Click File in the top-left corner of the Visual Studio Code header bar, and select Save.
Go to GitHub Desktop again and check if any conflicts still need to be resolved.
If a green checkmark is displayed next to the conflicted file name, the merge conflicts have been resolved. If no checkmark is displayed, you may have overlooked a merge conflict in your file.
If there are other conflicts that need to be resolved, select Open in Visual Studio Code again and repeat the previous steps until a green checkmark is displayed for all conflicted files.
Select Continue merge.
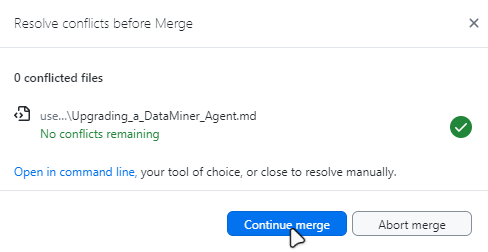
Click Push origin.
The number of local commits being pushed to GitHub may vary, depending on how outdated your current branch was.
Pull request shows an unusually high number of commits and changed files
Symptoms: You have made a pull request, but there is an unusually high number listed next to Commits and Files changed. The list of commits includes changes made by other contributors of the DataMiner documentation.
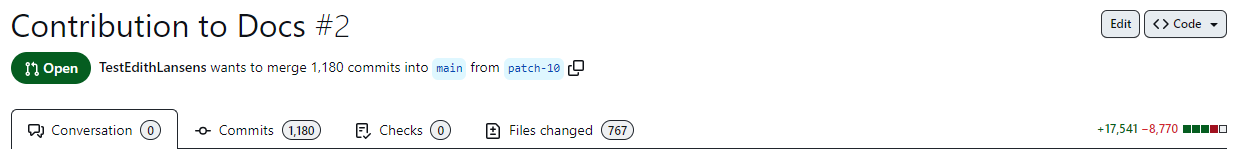
Cause: Your changes are being pushed to the wrong base repository. To verify whether this is the case, hover your mouse over main in [Your-GitHub-username] wants to merge # commits into main from [name-of-branch].
Correct:
SkylineCommunications/dataminer-docs:mainIncorrect:
[your-GitHub-username]/dataminer-docs:main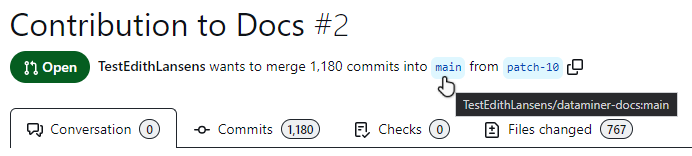
Resolution:
Scroll down and click Merge pull request.
Select Confirm merge.
In the top-left corner, click dataminer-docs.

Click the downwards arrow next to Contribute and select Open pull request.
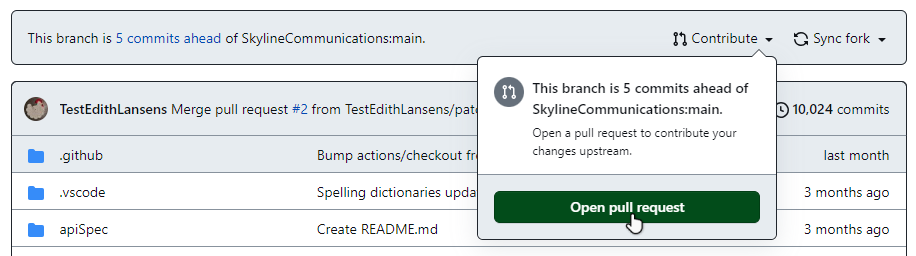
Ensure that the base repository you are merging to is
SkylineCommunications/dataminer-docs.
Enter a title and description for your changes and click Create pull request.
Note
Make sure the option Allow edits by maintainers is selected when you create the pull request, so that the documentation team will be able to correct any small issues (e.g. typos) directly.
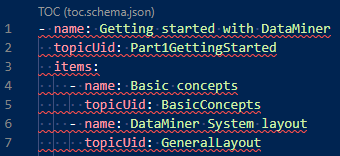
There is a duplicate item in the TOC even though it only occurs once in the toc.yml
Symptom: An item shows up twice in the table of contents even though it was only entered once in the toc.yml.
Resolution: Make sure there is no hyphen in front of the topicUid line. Only the name line should be preceded by a hyphen.
GitHub Desktop keeps basing branches on an outdated version of the main branch
Symptom: Newly created branches indicate that they were created a longer time ago.
Resolution:
Make sure your fork is up to date.
If you installed Git after you installed GitHub Desktop, remove the repository in GitHub Desktop and add it again.
GitHub Desktop throws "Author identity unknown" error
Symptom: When you try to push a commit using GitHub Desktop, this fails with the following error:
Author identity unknown
*** Please tell me who you are.
Run
git config --global user.email "you@example.com"
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
to set your account's default identity.
Omit ---global to set the identity only in this repository.
fatal: empty ident name (for <>) not allowed
Resolution:
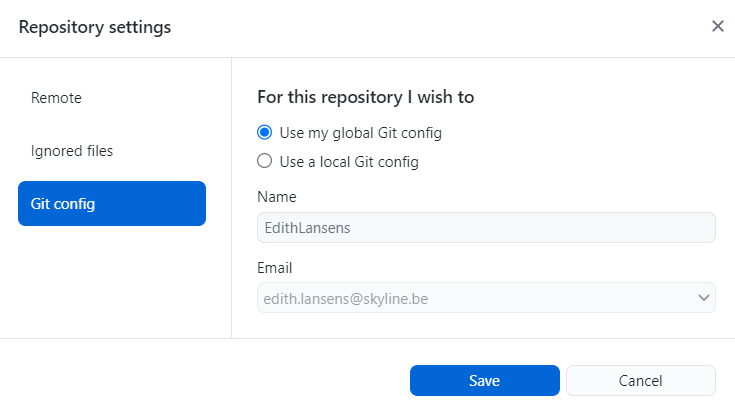
In GitHub Desktop, select Repository in the top-left corner and click Repository settings.
In the Git config tab, select Use my global Git config and click Save.
Other people are unable to make changes to your pull request
Symptom: You have made a pull request, but editors are unable to make direct changes to it, even though you want them to.
Resolution: This problem can have several solutions, depending on its cause.
Cause: The option Allow edits by maintainers was not selected when you created the pull request.
Resolution: Go to the pull request on GitHub, and make sure the option Allow edits by maintainers is selected.
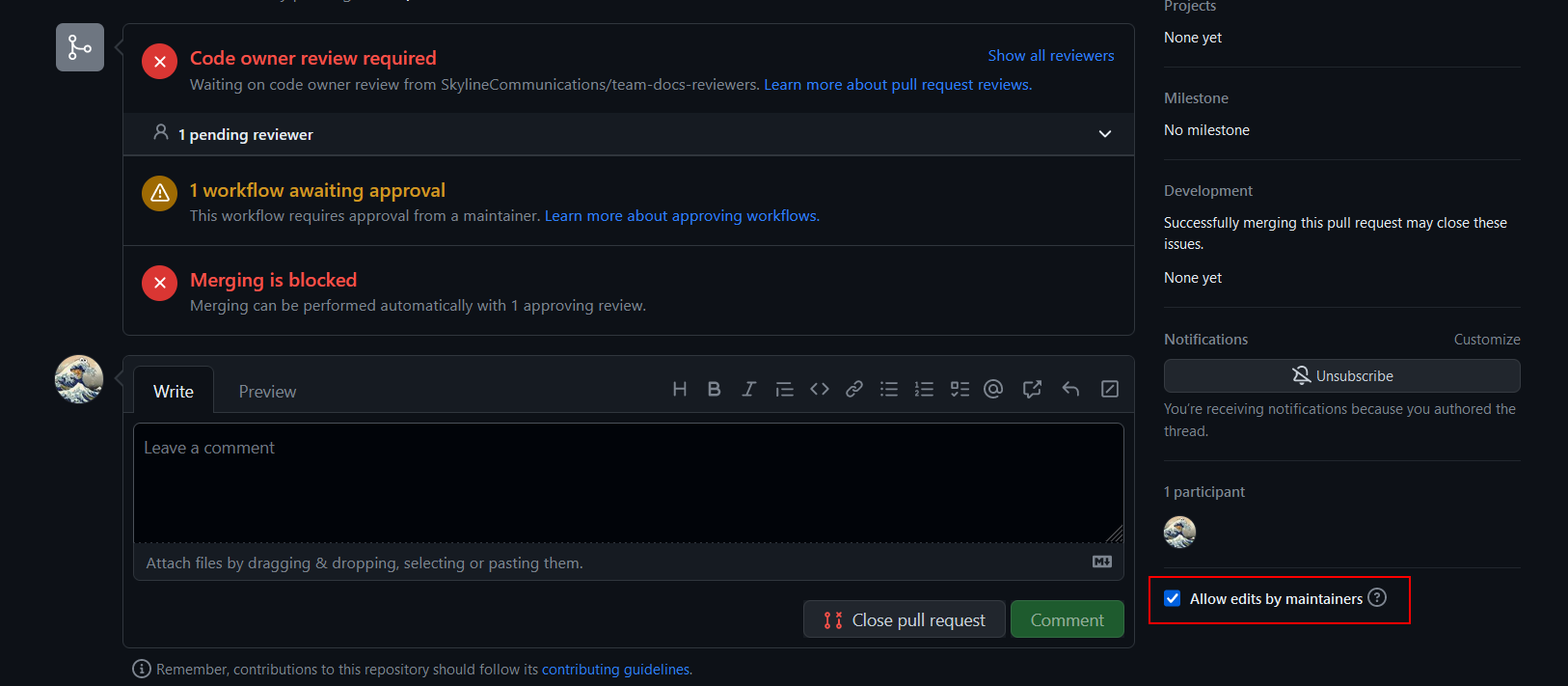
Cause: The branch you have used to create the pull request is protected.
Resolution: On the page for your fork on GitHub (i.e.
https://github.com/[Your GitHub handle]/dataminer-docs/), go to Settings > Branches, and check if you have enabled protection for the branch. If you have, disable this protection.
Issues when creating a test build
No instances of MSBuild could be detected
Symptom: When trying to create a build, you get the exception "No instances of MSBuild could be detected".
Resolution: If you only have .NET 7 installed, and not .NET 6, adjust the .csproj file in the build folder of the repository so that it targets "net7.0" instead of "net6.0".
Build failed because assembly or file could not be loaded
Symptom: When you try to create a test build, this fails with the following error:
Build failed.
[22-11-04 12:34:56.248]Warning:[ImportPlugins]Skipping file D:\DocFX\plugins_2xobfivj.yks\plugins\System.Memory.dll due to load failure: Could
not load file or assembly 'System.Memory, Version=4.0.1.2, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=cc7b13ffcd2ddd51' or one of its dependencies.
The located assembly's manifest definition does not match the assembly reference.
(Exception from HRESULT: 0x80131040)
Resolution: Install the latest version of DocFX.
Build failed because config or content files are missing
Symptom: When you try to create a test build, this fails with the following error:
Build failed.
[22-11-04 12:34:56.248]Error:Either provide config file or specify content files to start building documentation.
O Warning(s)
1 Error(s)
Resolution: This issue occurs if you try to make a build of only part of the repository. There are specific files in the root of the repository that are needed to be able to start building documentation, so make sure you always create your test builds based on the complete repository.
'UidNotFound' warnings and missing .NET API metadata during test build
Symptoms: When you try to create a test build, you consistently see warnings like the following:
C:\Users\[username]\Documents\dataminer-docs\develop\DSI\DSIOpenConfig\DSI_OpenConfig_Middleware.md:
warning UidNotFound: 3 invalid cross reference(s) "Skyline.DataMiner.DataSources.CommunicationGatewayMiddleware.Common.Api.DataSourceConfiguration",
"Skyline.DataMiner.DataSources.CommunicationGatewayMiddleware.Common.Api.DataSourceConfiguration.ClientCertificate",
"Skyline.DataMiner.DataSources.CommunicationGatewayMiddleware.Common.Api.ILogger".
Additionally, when generating metadata (e.g. using the docfx metadata command or the BuildDocs script), you get several warnings and errors, including:
No .NET API detected for .
Resolution: Install Visual Studio Build Tools 2022.
Recent changes do not show up in a build
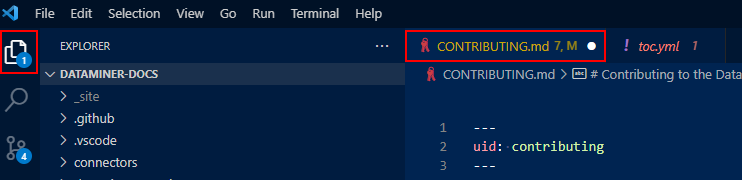
Symptom: When you create a test build, it does not include your recent changes.
Resolution: Make sure your changes are all saved. If the Explorer icon in the top-left corner shows a blue circle with a number in it, there are unsaved changes in a number of files corresponding with that number. The files that contain unsaved changes are marked with a white dot in the file header.
The template does not load correctly in the test build
Symptom: When you view your test build, it is not displayed correctly. Among others, no search box is available in the top-right corner.
Resolution: Install the latest version of DocFX.
Tip
You can use the command docfx --version to check which version is installed.
Note
If you have upgraded DocFX, but this upgrade does not seem to have taken effect, check whether you have a path parameter configured that leads to an older version. Go to Edit the system environment variables > Advanced > Environment Variables > System variables, select the Path parameter, if available, and click Edit. If an entry is listed that goes to a DocFX folder containing an old version of DocFX, delete that entry.