Workflow Designer app
The Workflow Designer has a central role in dataminer.MediaOps. It allows media engineers to define the technical workflows that are made available for both ad hoc and scheduled operations.
The main actions that users can do in the app include:
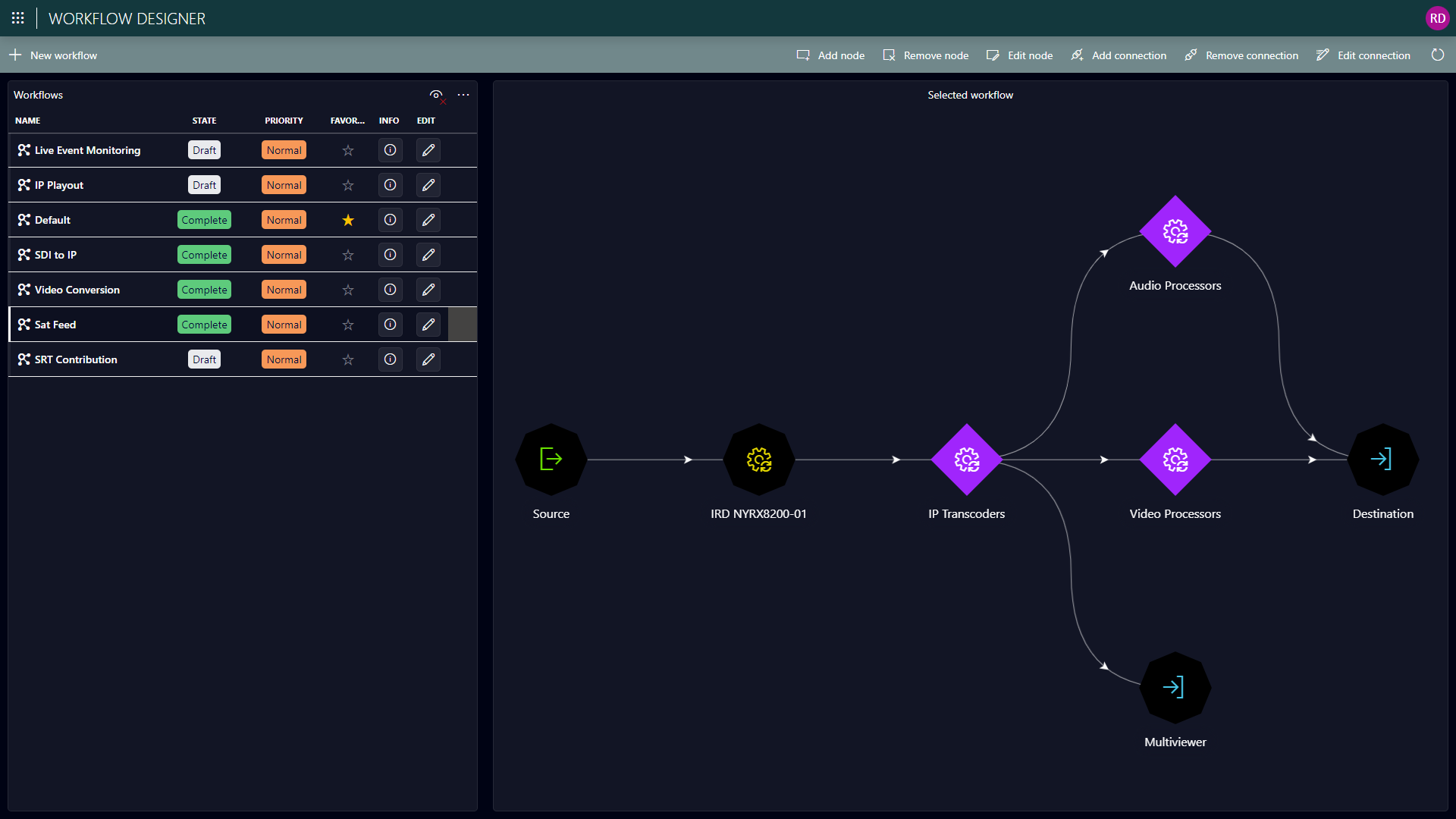
Adding nodes to a workflow. When a user creates a new workflow, the first thing they will typically do is add nodes representing the different actors that will contribute to the execution of the workflow.
Defining booking behavior. When workflows get executed, users can opt to create bookings on the nodes in the workflow.
Creating connections between nodes. The workflow designer allows users to define connectivity between nodes that need to have a network connection set up between them for the execution of the workflow.
Describing what should happen when a workflow gets executed.
Specifying monitoring settings.
Adding nodes to a workflow
In order to be of use, each workflow has to consist of at least one node. Four different types of nodes can be added to a workflow:
Source: Sources in a workflow refer to a source defined in the Virtual Signal Groups app. They can contain data that will be used to set up network connectivity as part of the workflow execution.
Destination: Similar to sources, destinations are defined in the Virtual Signal Groups app.
Resource: Resource nodes define everything that happens in a workflow between source and destination. Resources are defined in the resource studio and can represent network inventory managed with an element in DataMiner or any other real-world entities that are not managed by DataMiner, such as people, vehicles, rooms, etc.
Resource pool: Resource pools have the same purpose as resource nodes, but without the need to specify a specific resource instance. Instead they refer to a pool only, so that it is possible to select the specific resources at a later point in the workflow execution stage.
Each node that is part of a workflow also has several configuration options:
Optional alias for the node in the workflow. This can be useful if there are multiple nodes of the same type in a workflow
Include in booking: For resource or resource pool nodes, this determines whether node resources should be reserved when the workflow is executed.
Control script: The creator of a workflow can specify an interactive Automation script that operators will be able to quickly call upon from their control surfaces to do some predefined parameter control on the underlying network inventory managed via DataMiner.
Creating connections between nodes
Between workflow nodes that represent network inventory, connectivity may need to be set up in order to execute the workflow. For this, connections between the nodes can be defined. Each of these connections has a single source node and a single destination node. On top of that, they also have following properties:
Type: At present, only the Level-based type is supported. With this type, a connection will be made between the source and the destination based on their levels in the respective virtual signal groups.
Subtype: Within a level-based connection, there are several options for the exact connection execution:
All: All matching levels between source and destination will be connected.
Predefined subset: A subset of levels matching between source and destination can be connected. Users can choose between a number of predefined options, including "all video levels", "all audio levels", "all data levels", or any combination of these (e.g. all video and all audio levels).
Custom subset: Only a subset of levels matching between source and destination can be connected, which goes beyond the options available for a predefined subset. This can, for example, allow users to only connect the first audio level between source and destination.
Shuffle: The content of a level from the source can be connected to a different level on the destination. This can, for example, be used to connect the content of levels Audio 1 and Audio 2 on the source to levels Audio 3 and Audio 4 on the destination.
Execution order: This number determines the order in which the different connections defined in a workflow will be set up during the workflow execution.
Execution script
Note
If a workflow is called between a source and a destination that do not contain a sender and a receiver on one of the levels specified in these settings, nothing will be connected.
Describing workflow execution behavior
Workflows can be either executed ad hoc, when sources and destinations are connected in the Control Surface app, or scheduled, by planning a job based on a workflow in the scheduling app. The Workflow Designer app allows you to describe what needs to happen when a workflow execution is triggered. This is done by providing Automation scripts in two places:
Workflow execution script: This script describes the overall execution logic of the workflow. The script will always be triggered by the system when a workflow is executed, whether this is ad hoc or scheduled.
The dataminer.MediaOps installation package comes with a default workflow execution script called Workflow.Default:
For all nodes of type "resource pool" in the workflow, this script will find a resource that is available from that pool.
The script will iterate over the connections of the workflow in the "execution order" and trigger the "execution script" defined on the connections.
Connection execution script: This is an optional property of all connections in a workflow. It can be used to describe what exactly needs to happen when the source of the connection is connected to its destination.
The dataminer.MediaOps installation package comes with a default connection execution script called Workflow.Connection.Default. This script will connect the source and destination as described by the connection's type and subtype. By tweaking this script, you can change that behavior or add additional logic to it.
Note
Contrary to the workflow execution script, there is no guarantee that the system will always execute the connection execution script. If you change the content of the workflow execution script, it is your responsibility to make sure the connection execution script is still executed for every connection in the workflow if needed.