Parameters
Parameter types
A protocol parameter is a versatile component. A parameter can represent a table, a table column, an internal placeholder to hold a value (e.g., a counter, a buffer), a UI component (e.g., a button), etc.
Note
For an overview of how to define UI components in a DataMiner protocol, see UI components.
The following subsections introduce the different types of parameters that are defined in DPML
Read, write, fixed, and dummy parameters
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| read | Used as a data placeholder. |
| fixed | Used to define a value that will not change. |
| dummy | Used as a data placeholder for which the actual data is of no interest, e.g., to trigger a QAction. |
| write | Typically used to create a write overlay of a read parameter, or to define a button. |
A parameter of type read is typically used as a data placeholder for internal logic (e.g., to hold a value of counter of serving as a buffer) or for defining a UI component (e.g., a label).
A fixed parameter acts as a data placeholder that will not change. Though it is in fact possible to change the value of a fixed parameter (using a change length action and then setting the new value), this is not a common operation. For example, to define a parameter that represents a fixed value used in a communication protocol that is being implemented, a fixed parameter can be defined as follows:
<Param id="11">
<Name>Fixed_0x0A</Name>
<Description>Fixed 0x0A</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>fixed</LengthType>
<Length>1</Length>
<Value>0x0A</Value>
</Interprete>
</Param>
In the example above, the Interprete tag is used to define the length of the fixed parameter and the value. For more information, see Protocol.Params.Param.Interprete.
A parameter of type dummy is typically used to hold data that is not of real interest, e.g., to hold part of the response that is not processed or to trigger a QAction.
Note
The units of measure for numeric parameters can be automatically adjusted to a more readable format if the dynamic units feature is enabled. This depends on the DataMiner version and the configuration of the DynamicUnits element. See DynamicUnits.
Element information
The following parameter types can be used to obtain element-related information as specified in the element wizard:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| bus | Holds the bus address as specified in the element wizard. |
| elementdmaid | Parameter containing the DMA ID and element ID of the DMS element. |
| elementid | Parameter containing the element ID of the DMS element. |
| elementname | Parameter containing the element name of the DMS element. |
| ip | Contains the IP addresses and port numbers of the connections defined in the protocol. |
| pollingip | Holds the IP addresses of the connections defined in the protocol. |
For example, to define a parameter that holds the combination DMA ID/element ID, you can define a parameter as follows:
<Param id="48">
<Name>GlobalElementID</Name>
<Description>Global Element ID</Description>
<Information>
<Subtext>The global element ID. Format: {dmaID}/{elementID}</Subtext>
</Information>
<Type>elementdmaid</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
</Param>
Note
- The value of these parameters is filled in by the DataMiner software. It is not possible to use a trigger on value change on these parameters to capture the value set by software.
- Parameters of type "elementdmaid", "elementid" or "elementname" cannot be displayed. To show the values of these parameters, define a parameter of type "read" and perform a "copy" action to copy the value of one of these parameters to the "read" parameter. Alternatively, a SendToDisplay method call (SLProtocol) can be used.
- If you want to use the bus address in a command, the command could require either a decimal value or a hex value. Depending on the required format, you can use these Interprete values:
- Bus address is a decimal value, command needs hex bytes Example: bus=23133 use in Interprete: unsigned number, length 2, base 16, double -> bytes = 5A5D (hex values of bus address)
- Bus address contains hex values, command needs ASCII bytes example: bus=5AFF use in Interprete: numeric text, length 4, string -> bytes = 35414646 (ASCII values of bus address)
- When multiple connections are defined, the parameters of type "ip", "pollingip" and "bus" will show a semicolon-separated list of values.
DataMiner Agent information
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| dataminer info | Parameter holding general DataMiner information. |
Note
- The value of these parameters is filled in by the DataMiner software. It is not possible to use a trigger on value change on these parameters to capture the value set by software.
- Parameters of types specified in this section cannot be displayed. To show the values of these parameters, define a parameter of type "read" and perform a "copy" action to copy the value of this parameter to the "read" parameter. Alternatively, a SendToDisplay method call (SLProtocol) can be used.
Internal parameters
When a protocol is developed, a number of building blocks such as parameters, actions, triggers, etc. are specified. In addition to the parameters defined by the developer, a number of general internal parameters are defined for each element. These general parameters are all defined in the 65000 range. For an overview of these parameters, refer to Reserved parameter IDs.
The configuration of these parameters for an element is displayed on the [GENERAL PARAMETERS] page of the element:
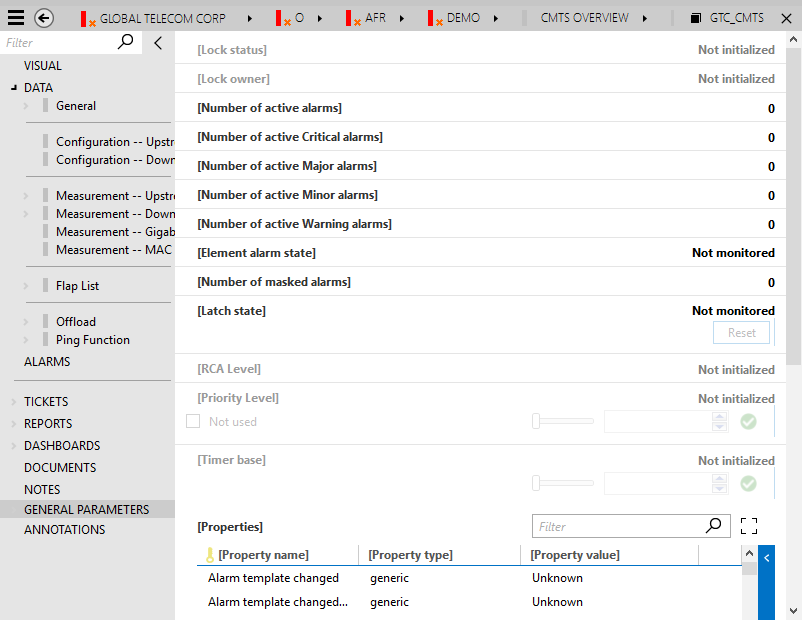
The general parameters are organized into four groups: communication, DCF, replication, and verification.
General parameters can be loaded dynamically, and the following defaults apply:
- Communication: General parameters belonging to this group are not loaded for protocols of type http, websocket, opc, gpib, virtual, sla, and service.
- DCF: Only loaded if parameter groups are defined in the protocol.
- Verification: General parameters belonging to this group are not loaded when MaintenanceSettings.xml has been configured to enable Command Execution Verification. (With the ProtocolSettings.ExecutionVerification tag.)
- Replication: By default, general parameters belonging to this group are always loaded.
You can override the above-mentioned default behavior by adding a GeneralParameters tag to the protocol. In this tag, you can specify for each of the different types of general parameters whether you want these added to elements based on the protocol in question. Refer to Protocol.GeneralParameters in the DataMiner Protocol Markup Language section for more information.
Other parameter types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| array | Defines a table. See Table. |
| discreet info | Receives notifications of matrix configuration changes. See Discreet info. |
| crc | Used for Cyclic Redundancy Check calculation. See Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). |
| group | See Write bit. |
| header | Parameter used to define the beginning of a frame. See Header and trailer. |
| length | Parameter used to hold the length of a frame. See Response matching. |
| read bit | Parameters of type "read bit" retrieve data from a group. See Read bit. |
| response | A parameter that contains multiple bytes can be split up into smaller pieces when it refers to another response. See Parameters of type response. |
| trailer | Parameter used to define the end of a frame. See Header and trailer. |
| write bit | Parameters of type "write bit" change data in the group. See Write bit. |
Parameter change events
When a parameter change triggers (e.g., when a protocol.SetParameter call is performed), the following steps are executed:
- If there are triggers that trigger on a change of the parameter, these are executed. If there are no triggers defined that trigger on this parameter, but there are triggers defined that trigger on each parameter change (i.e., Trigger\On is set to "each"), these are executed.
- If the parameter has one of the following options: ssh username, ssh password, ssh options, dynamic ip, then this setting is updated.
- If the parameter has Param@save set to
true, the value is saved. - If the parameter has Param@setter set to
true, the value gets copied to the corresponding read parameter. - If snmpSet, snmpSetAndGet, snmpSetWithWait or snmpSetAndGetWithWait is used, the corresponding SNMP operation is executed.
- If there are QActions that trigger on this parameter QAction@triggers, these are executed.
- If data distribution is configured (Param/Type@distribution), the value is distributed.
- If the dynamic SNMP Get option or dynamicSnmpGet is used, the SNMP get is scheduled.
Note
The SLProtocol.SetParameterBinary method (or Notify 177 NT_SET_BINARY_DATA) does not trigger change and therefore does not execute the steps mentioned above.