General Main Release 10.3.0 – Highlights
Note
For known issues with this version, refer to Known issues.
Tip
For release notes related to DataMiner Cube, see DataMiner Cube 10.3.0.
Highlights
DMS core functionality
BREAKING CHANGE: GetSpectrumTrendTraceDataMessage will now always require a time range [ID 31402] [ID 32016]
When a GetSpectrumTrendTraceDataMessage was used to retrieve spectrum data, up to now, it was possible to pass an optional time range (i.e. RangeStart and RangeEnd) next to an ID (i.e. RecordID). From now on, passing a time range next to an ID will be mandatory.
DataMiner Object Models: Defining a TLL for DomTemplates, DomInstances and DomInstance history [ID 32662]
It is now possible to define a "time to live" property for the following types of DomManager objects:
| Object type | Property |
|---|---|
| DomInstance | DomInstanceTtl |
| DomTemplate | DomTemplateTtl |
| HistoryChange (DomInstanceHistory) | DomInstanceHistoryTtl |
Times are defined as TimeSpan objects. By default, these will be set to TimeSpan.Zero, i.e. no TTL. When, for a particular type of object, the TTL is set to e.g. 1 year, those objects will be automatically removed when they were last modified more than a year ago.
Example:
var moduleSettings = new ModuleSettings("example")
{
DomManagerSettings = new DomManagerSettings()
{
TtlSettings = new TtlSettings()
{
DomTemplateTtl = TimeSpan.Zero, // No TTL
DomInstanceHistoryTtl = TimeSpan.FromDays(365), // 1 Year
DomInstanceTtl = TimeSpan.FromDays(730) // 2 Years
}
}
};
Note
TTL settings are checked every 30 minutes. When you configure a very short TTL (e.g. 15 minutes), keep in mind that the objects in question will only be removed during the next cleanup cycle.
OpenSearch & Amazon OpenSearch Service [ID 34651]
It is now possible to install a dedicated OpenSearch indexing database cluster as an alternative for Elasticsearch. This indexing cluster also requires a Cassandra cluster.
At present, all OpenSearch versions are supported:
- 1.X
- 2.X
For more information on setup and configuration, see OpenSearch database.
Note
It is also possible to use Amazon OpenSearch Service on AWS as an alternative to an on-premises hosted Elasticsearch/OpenSearch cluster. For more information on setup and configuration, see Amazon OpenSearch Service.
Amazon Keyspaces [ID 34872]
It is now possible to use the Amazon Keyspaces Service on AWS as an alternative for a Cassandra Cluster setup.
Note
- Amazon Keyspaces does not support all Cassandra functionality, most notably indices on columns. As a result, some queries against logger tables (including SLAs) may be slower on Amazon Keyspaces compared to Cassandra.
- The only consistency level supported is
Local Quorum. See Supported Apache Cassandra consistency levels in Amazon Keyspaces. No matter the configuration, the consistency level will always be overwritten toLocal Quorum. - The only replication strategy supported is the Amazon Keyspaces specific
Single-Region strategy, which is not configurable. - Migrating existing databases to Amazon Keyspaces is not yet supported.
For more information on setup and configuration, see Amazon Keyspaces Service.
DMS Security
SLSSH: Enhanced HMAC, cypher and key exchange algorithm support [ID 32664] [ID 32786]
SLSSH now supports the following additional HMAC, cyphers and key exchange algorithms:
- HMAC-SHA2-512
- AES256CRT
- ECDHSHA2NISTP384
- ECDHSHA2NISTP521
DataMiner now supports the encryption methods detailed below (in order of preference).
HMACs
- HMAC-SHA2-512
- HMAC-SHA2-256
- HMAC-SHA1
- HMAC-MD5
Key exchange algorithms
- ecdh-sha2-nistp521
- ecdh-sha2-nistp384
- ecdh-sha2-nistp256
- diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
- diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
- diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1
Ciphers
- Aes-256-CTR
- Aes-128-CTR
- Aes-128-CBC
- 3des-CBC
SLSSH: Enhanced host key verification algorithm support [ID 33132]
When acting as an SSH client, DataMiner now supports the following host key verification algorithms (in order of preference):
- ecdsa-sha2-nistp521 (new)
- ecdsa-sha2-nistp384 (new)
- ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 (new)
- ssh-rsa
- ssh-dss
DMS Protocols
Timers: Specifying an interval between two consecutive ping packets [ID 34463] [ID 34549]
When you configure a timer to automatically send ping requests to a device, you can now use either the interval option or the intervalPid option to specify the interval in ms between two consecutive ping packets.
interval: With this option, you can specify a fixed interval in ms between two consecutive ping packets. This should be used when the device does not respond to all ping requests when they are sent without any interval.intervalPID: Instead of specifying a fixed interval value ("interval=x"), it is also possible to specify a dynamic value stored in a parameter. Note that if you specify both a fixed and a dynamic value, the latter will take precedence.The value in the referred parameters must not be 0 or uninitialized. Otherwise, 0, the hard-coded value on the timer, or the last valid value will be used by default. The referred parameters must be of numeric type.
Note
These options are only relevant when amountPackets or amountPacketsPID is used. These are currently only supported in conjunction with the threadPool option. When threadPool is not used, only one ping request will be sent.
DMS Service & Resource Management
Replacing system functions by uploading an XML file [ID 32264]
It is now possible to replace the system protocol functions by uploading an XML file using the ProtocolFunctionHelper. See the following example.
var pfHelper = new ProtocolFunctionHelper(engine.SendSLNetMessages);
var xmlContent = File.ReadAllText("...");
pfHelper.ReplaceActiveSystemFunctionDefinitions(xmlcontent);
Note
- If the uploaded file is not a valid XML file, a DataMinerException will be thrown and the system functions will not be replaced.
- Each function in the XML file must have a valid ID. Functions without a valid ID will be ignored.
Modified AbsoluteQuarantinePriority behavior and several new SRM features [ID 32654]
Several changes to the SRM framework have been introduced:
- Modified AbsoluteQuarantinePriority behavior.
- New ConcurrencyUsageType property for ResourceUsageDefinition
- Possibility to book complete resource capacity
- Possibility to include elements in bookings
Modified AbsoluteQuarantinePriority behavior
The behavior of the AbsoluteQuarantinePriority property has been modified. Up to now, if this property was set to true for a booking instance, all overlapping booking instances using the same resources were forced into quarantine. Now this property will only determine the priority of the booking when a quarantine is needed.
To implement a quarantine, overbooked capacity is now removed from bookings according to the following order of priority:
- Bookings that are already in the quarantined state.
- Bookings for which AbsoluteQuarantinePriority is not specified or false.
- Bookings that are in a "Pending" state.
- Bookings with the latest start time.
- Booking of which the name comes last alphabetically.
- Bookings of which the GUID comes last alphabetically.
The image below illustrates a situation where the quarantine behavior has changed. Previously, booking A would have been quarantined, as it uses resource 1. Now this will no longer happen as the capacity is actually not overbooked.
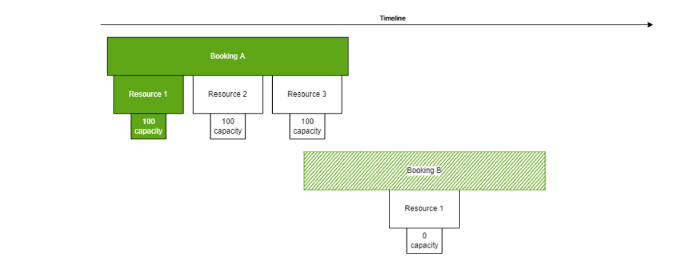
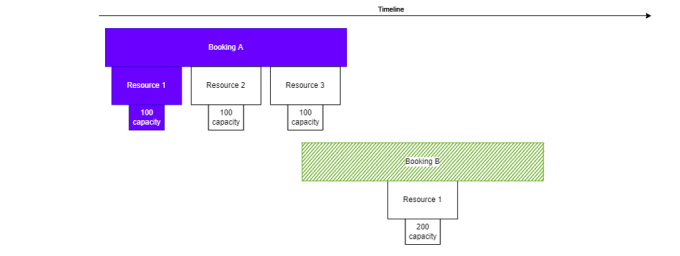
The following image also illustrates the modified behavior. If booking B does not have AbsoluteQuarantinePriority set to true, its capacity will be moved, as it has a later start time. If AbsoluteQuarantinePriority is set to true, the overbooking will be resolved by moving the capacity from booking A.
New ConcurrencyUsageType property for ResourceUsageDefinition
A ResourceUsageDefinition now has the property ConcurrencyUsageType, which can have the following values:
- ConcurrencyUsageType.Default: The default value. The ResourceUsageDefinition takes one concurrency of the resource.
- ConcurrencyUsageType.All: The ResourceUsageDefinition takes all the concurrency of the resource.
- ConcurrencyUsageType.None: The ResourceUsageDefinition does not take any concurrency of the resource.
Resource usage can only overlap with a ResourceUsageDefinition with ConcurrencyUsageType.All if it is set to ConcurrencyUsageType.None. This limitation is also in place for a single booking: if a booking has a resource with complete concurrency and another resource with 1 concurrency, the booking will be quarantined because it requests more concurrency than is available. If a complete concurrency usage is quarantined to resolve a concurrency conflict (as determined by the priority defined on booking level), it will be moved in its entirety – there is no option to only move part of the concurrency to quarantine.
The actual concurrency of a ResourceUsageDefinition with ConcurrencyUsageType.All is determined at runtime, as the MaxConcurrency value of the resource at the moment when it is needed, e.g. when GetEligibleResources is called or when quarantine checks are done to add or update a booking instance or resource.
Code example:
var booking = new ReservationInstance(new TimeRangeUtc(DateTime.UtcNow, DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(10)))
{
Name = "Booking 123",
ID = Guid.NewGuid()
};
var resourceUsage = new ResourceUsageDefinition(resourceId)
{
ConcurrencyUsageType = ConcurrencyUsageType.All
};
booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance.Add(resourceUsage);
Booking complete resource capacity
It is now possible to book all the capacities of a resource for their complete value, by setting the UsesCompleteCapacity property for the ResourceUsageDefinition to true. If the resource has more than one capacity defined, this will reserve all capacities. By default, this property is set to false.
No other usage can overlap in case complete capacity is used. This limitation is also in place for a single booking: if a booking has a resource with complete capacity and another resource with 100 capacity, the booking will be quarantined because it requests more capacity than is available. If a complete capacity usage is quarantined to resolve a conflict (as determined by the priority defined on booking level), it will be moved in its entirety.
The actual capacity in case UsesCompleteCapacity is true is determined at runtime, e.g. when GetEligibleResources is called or when quarantine checks are done to add or update a booking instance or resource.
Code example:
var booking = new ReservationInstance(new TimeRangeUtc(DateTime.UtcNow, DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(10)))
{
Name = "Booking 123",
ID = Guid.NewGuid()
};
var resourceUsage = new ResourceUsageDefinition(_resource.ID)
{
UsesCompleteCapacity = true
};
booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance.Add(resourceUsage);
Including elements in bookings
It is now possible to define an ElementUsageDefinition to include an element in a booking. When the element is included, ResourceUsageDefinitions will automatically be added for all the resources linked to the element. These resources will have the new IsAutoGenerated property set to true.
ElementUsageDefinition has three properties:
ElementUsageImpact: Determines if the element can be used in overlapping bookings. If set to None, overlapping bookings can use the same element. If set to Full (the default value), no overlapping bookings can use the same element, even if they have impact None. If the AddOrUpdateReservationInstances call fails because there are overlapping bookings using the same element with Full impact, no changes will be saved and an error of type ElementUsageOverflow will be returned.
IncludeCapacityBehavior: Can be set to All or None. If this is set to All, the generated ResourceUsageDefinitions will have the UsesCompleteCapacity property set to true.
IncludeConcurrencyBehavior: Can be set to All or None. If this is set to All, the generated ResourceUsageDefinitions will have the ConcurrencyUsageType property set to ConcurrencyUsageType.All.
Code example:
var booking = new ReservationInstance(new TimeRangeUtc(DateTime.UtcNow, DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(10)))
{
Name = "Booking 123",
ID = Guid.NewGuid()
};
var elementUsage = new ElementUsageDefinition(new ElementID(123,456))
{
ElementUsageImpact = ElementUsageImpact.Full,
IncludeCapacityBehavior = IncludeCapacityBehavior.All,
IncludeConcurrencyBehavior = IncludeConcurrencyBehavior.All
};
booking.ObjectUsages.Add(elementUsage);
The following resources are added when an element is included in a booking:
- Resources that reference the element with the DmaID and ElementID properties.
- Function resources that have the referenced element as their parent element (based on MainDveDmaId and MainDveElementId properties).
- Virtual function resources linked to the element (based on PhysicalDeviceDmaId and PhysicalDeviceElementId properties).
Whenever the booking is updated or a relevant resource is created or updated, the element usage is automatically updated. Any changes you do to auto-generated usage will be overwritten by the core software. When the auto-generated usage is updated, the TraceData of the AddOrUpdateResource call will contain ResourceManagerInfoData of type ResourceUsagesGeneratedForReservationInstances.
The deletion of resources in auto-generated bookings is blocked in the same way as deletion of resources that were not added automatically is blocked.
This new feature has an ElementUsages exposer, which can be used to filter bookings that include a certain element. For example:
var elementToSearchFor = new ElementID(123, 789);
var filter = ReservationInstanceExposers.ElementUsages.Contains(elementToSearchFor.ToString());
var bookings = rmHelper.GetReservationInstances(filter);
Functions.xml file: Assigning a function type to a function [ID 32851]
It is now possible to assign a function type to each function defined in a functions.xml file.
A function can be assigned one of the following types:
- UserTask
- ScriptTask
- ResourceTask
- Gateway
- NoneStartEvent
- TimeStartEvent
- EndEvent
Default function type: NULL
Example:
<Functions>
<Function id="..." name="..." maxInstances="..." profile="...">
...
<FunctionType>UserTask</FunctionType>
</Function>
...
</Functions>
Note
If you add a <FunctionType> element inside a <Function> element, it must be the last child element inside the <Function> element.
BREAKING CHANGE: Removing a Resource or ResourcePool object will now always require a valid ID [ID 33836]
Up to now, it was possible to delete Resource and ResourcePool objects in a filtered way by passing an “incomplete” object to the associated remove method of the ResourceManagerHelper. Moreover, passing an empty list or NULL would remove all resources on the system. This will no longer be possible.
From now on, it will only be possible to remove Resource objects by ID or name (case sensitive) and ResourcePool objects by ID.
When DataMiner detects a remove request that contains an object with an empty ID (and an empty name in case of a request to remove a Resource object, one of the following messages will be added to the ResourceManager.txt log file (type: info):
In case of a request to remove a Resource object:
Detected a resource delete request that contained at least one object without an ID. Deleting resources with resource object filters is not supported anymore.In case of a request to remove a ResourcePool object:
Detected a resource pool delete request that contained at least one object without an ID. Deleting resource pools with object filters is not supported anymore.
Note
From now on, the log entries added when creating or deleting resources or resource pools will no longer contain the IDs of all objects that were created or deleted. Instead, they will only contain the IDs of the first 10 objects that were created or deleted.