Verifying Elasticsearch synchronization
Important
Elasticsearch is only supported up to version 6.8, which is no longer supported by Elastic. We therefore recommend using Storage as a Service instead, or if you do want to continue using self-managed storage even though this is not recommended, using OpenSearch.
Checking database health
Elasticsearch Cluster Monitor
In Cube, open the element card of the element using the Elasticsearch Cluster Monitor protocol and select DATA in the tree view in the navigation pane on the left. Select the general data display page and verify whether the following is displayed correctly:
Connection Status: Success
Cluster Status: All primary and replica shards are active or All primary shards are active, but not all replica shards are active
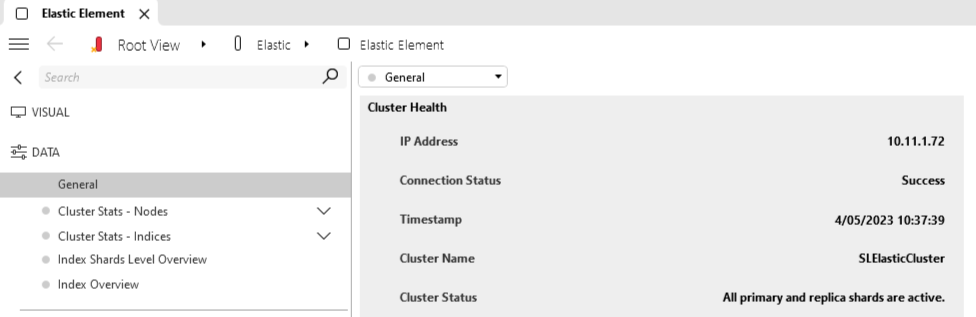
Make sure the element is not in timeout.
Elasticsearch API
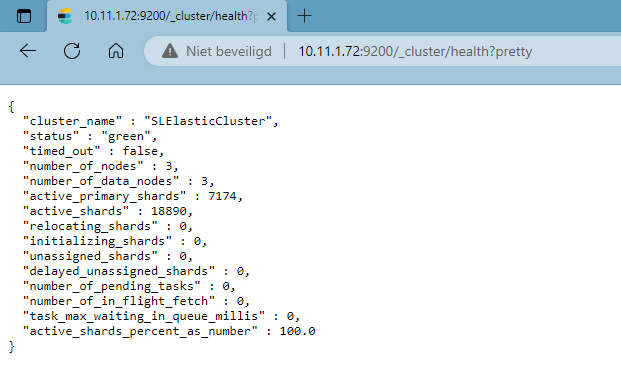
Enter
[ELASTIC NODE IP]:9200/_cluster/healthin your browser's address bar.Ensure that the status is set to green or yellow.
Ensuring matching index names
Elasticsearch Cluster Monitor
In Cube, open the element card of the element using the Elasticsearch Cluster Monitor protocol and select DATA in the tree view in the navigation pane on the left. Select the Index Overview data display page.
Retrieve all values in the Name [IDX] column.
Repeat these steps for the second database.
Make sure that the strings are identical across the databases.
Elasticsearch API
Enter
[IPADDRESS]:9200/_cat/indices?v&s=index:descin your browser's address bar; e.g.1.2.3.4:9200/_cat/indices?v&s=index:desc.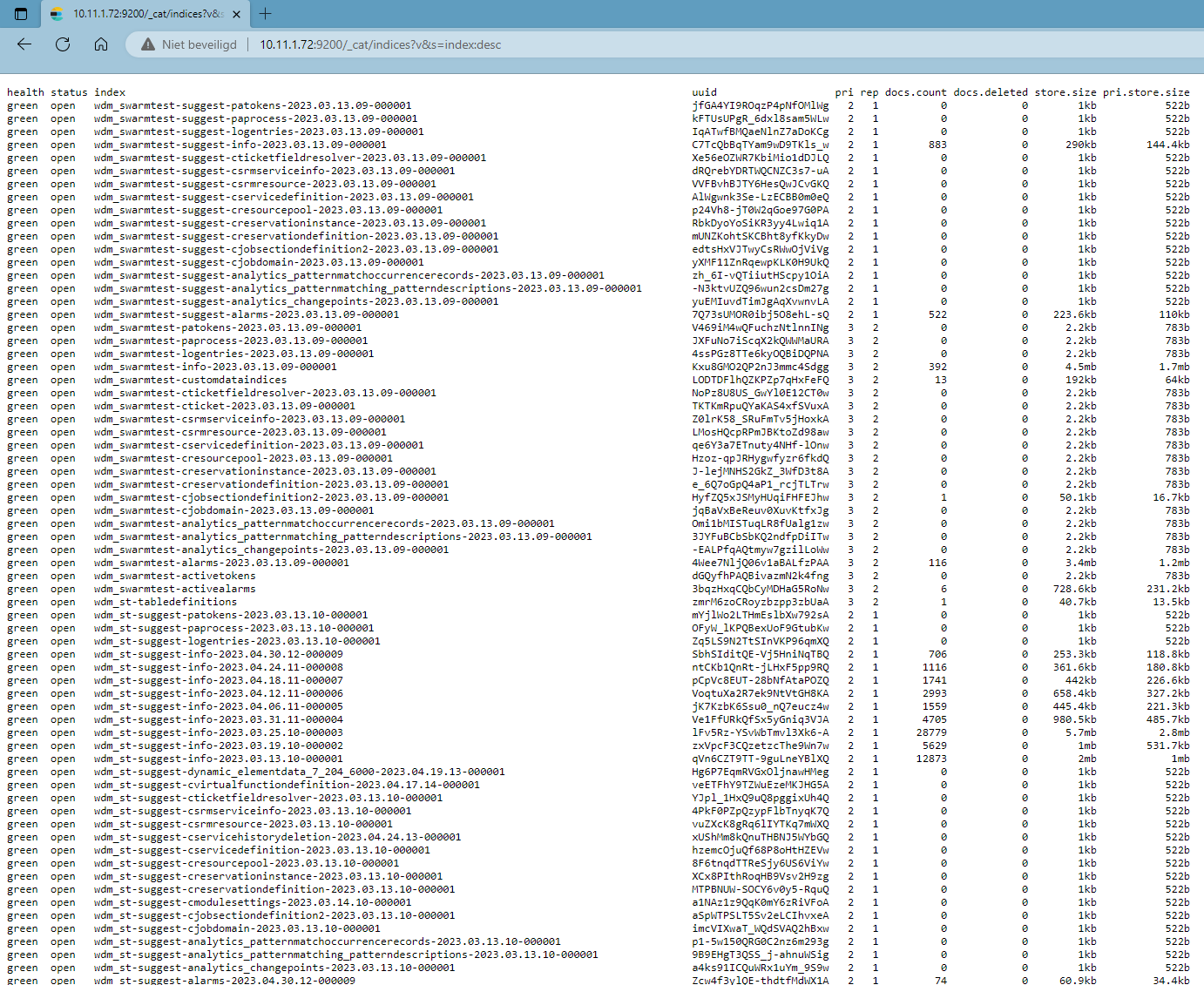
Get all values in the index column.
Repeat these steps for the second database.
Make sure that the strings are identical across the databases.
Note
If one of the databases was added later than the first database, you can no longer rely on the index counter as indices may have different sequence numbers because of the newest node missing certain Elasticsearch rollovers. Even though the Elasticsearch rollover API is called at the same time, it can produce a different sequence number. While most of the data will be synchronized, we do not support the situation. If you find yourself in this situation, the best course of action is to restore the data to the oldest Elasticsearch node by following the Taking a snapshot of one Elasticsearch cluster and restoring it to another Method of Procedure.
Ensuring matching index sizes
Data loss can occur because of factors like packet loss while being transported toward the database. This can cause slight differences in the document count. Therefore, it is important to not expect the document count to be 100% identical.
The number of differences that is allowed depends on several things, e.g. the place where these differences occur. A suggest index can be absent and not pose a significant threat to the system. However, an active-alarms index or an index that holds data for your SRM app may not be expendable. See Index types.
Index types
This is an overview of the different indices and the functionalities they are required for so that you can focus on the indices important to your situation.
Indices related to search suggestions
These indices contain data for enhanced search suggestions and can usually be omitted without affecting other parts of the software. Note that these are not related to the suggestion events generated by DataMiner's Augmented Operations features.
[prefix]-suggest-info[prefix]-suggest-alarms[prefix]-suggest-…
Indices related to Low-Code Apps and DOM
These indices are mandatory when using Low-Code Apss or DOM.
[Prefix]-cdom…:[Prefix]-cdomtemplate_[Template_name][Prefix]-cdomsectiondefinition_[Template_name][Prefix]-cdominstance_[Template_name][Prefix]-cdomdefinition_[Template_name][Prefix]-cdombehaviordefinition_[Template_name]
SRM-related indices
These indices are mandatory when using SRM apps. Without these indices, SRM will not work.
[Prefix]-csrmserviceinfo-...[Prefix]-cservicedefinition-...[Prefix]-creservationinstance-...[Prefix]-creservationdefinition-...[Prefix]-cjobsectiondefinition2-...[Prefix]-cjobsectiondefinition-...[Prefix]-cjobdomain-...[Prefix]-cjob2-...[Prefix]-cjob-...
Alarm-related indices
[Prefix]-activealarms: Contains active alarms. If this index is emptied, alarms might be recreated with new alarm IDs.[Prefix]-alarms: Contains other alarms. If this index is emptied, the alarm data in general will be gone, including (but not limited to) history alarms.
Indices related to information events
[Prefix]-info: Contains the information events. If this index is emptied, information events will be gone. This will usually not have a significant impact on the performance of the system, but could overwrite certain useful information, such as users logging in, etc.
Elasticsearch Cluster Monitor
Go to the element card of both Elasticsearch elements and select the Index Overview page under DATA in the tree view in the navigation pane on the left.
Check whether the Store Size and Documents Count have a similar number. As mentioned above, these numbers might not be completely identical and small differences may be tolerated.
Tip
To compare the Store Size and Documents Count more quickly, adjust the Documents Count column so it is sorted in descending order.
Elasticsearch API
Enter
[IPADDRESS]:9200/_cat/indices?v&s=index:descin your browser's address bar, e.g.1.2.3.4:9200/_cat/indices?v&s=index:desc.Ensure that the
store.sizeanddocs.counthave a similar number.Note
These numbers will not match up completely and small differences may be tolerated.
Tip
To compare the
store.sizeanddocs.countmore quickly, enter[IPADDRESS]:9200/_cat/indices?v&s=docs.count:descin your browser's address bar so thedocs.countcolumn is sorted in descending order.