Quarantine
About the quarantine state
The quarantine state is a special state of a booking, which indicates that the booking cannot start because one or more resources that were assigned to it are no longer available. Bookings are automatically moved to this state when Resource Manager detects such a situation.
Usually, this happens when a booking is added or edited so that overlapping bookings use the same resource, and the resource does not have enough capacity or concurrency to support all bookings.
If a booking is in the quarantine state, the IsQuarantined flag is set to true on the corresponding ReservationInstance object, and the state of the booking will be set to Pending. Such bookings will still reserve the non-quarantined resources, in the same way as if they were in the regular Pending state. The resources that are no longer available are included in the QuarantinedResources collection of the booking, along with some information about why these resources have been moved to quarantine.
Examples
Concurrency conflict
Consider a system that has a booking with two resources Resource A and Resource B. Each resource in this system has a maximum concurrency of one, so it can only be used by one booking at the same time.

If a second booking is added to the system that overlaps with the first booking and that also wants to use Resource A, there will be a scheduling conflict. Resource A does not have enough concurrency to support the second booking. If the addition of the second booking is forced anyway, Resource Manager will resolve the conflict as follows:
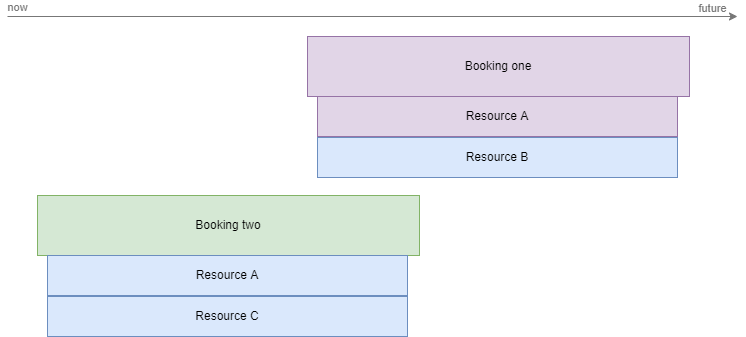
In the diagram above, Booking one has been moved to quarantine, because it has the lowest priority (see Quarantine priority). Booking one will not start until the quarantine conflict is resolved. However, Resource B remains assigned to Booking one, which means that if another booking is created that overlaps with Booking one and that tries to use Resource B, another scheduling conflict will arise.
Capacity conflict
Consider a system that has two existing bookings in the confirmed state, each using a resource Resource A. Resource A has a concurrency of 10, so it can be used by 10 bookings at the same time, and it has a capacity defined with a maximum bookable value of 10.
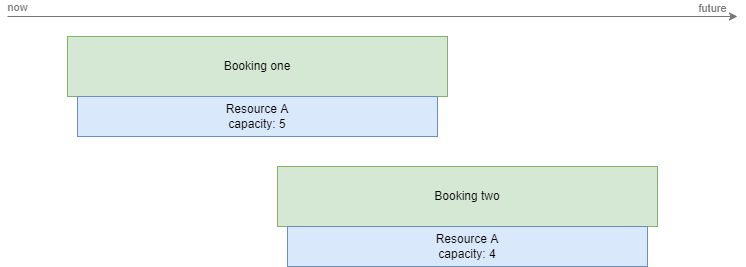
If a third booking is added as configured below, there is not enough capacity on Resource A to support this booking. If the addition of Booking three is forced anyway, Resource Manager will resolve the conflict as follows:
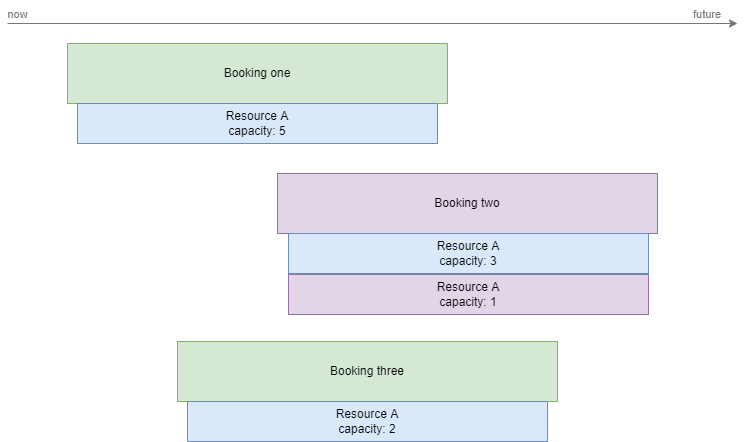
In the diagram above, Booking two has been moved to quarantine, because it has the lowest priority (see Quarantine priority). Resource A is still partially assigned to Booking two, because only the capacity necessary to resolve the conflict has been moved to quarantine. Since Resource A has a capacity of 10, only 1 capacity needed to be moved.
Quarantine priority
When Resource Manager detects that some usage will need to be quarantined in order to resolve a conflict, it will remove usage from bookings according to a set priority. The priority of a booking is determined as follows:
Quarantined bookings
Bookings that are already in quarantine have the lowest priority and will be the first to have their resource usage removed.
Bookings with HasAbsoluteQuarantinePriority flag
Bookings with the HasAbsoluteQuarantinePriority flag set have the highest priority, unless they are already in quarantine. The usage of these bookings will be moved last when resource usage needs to be moved to resolve scheduling conflicts.
Bookings in the Pending state
Bookings that are in the Pending state have a lower priority and will have their resource usage removed before other non-quarantined bookings.
Start Time
Among bookings in similar states, those with a later start time will have a lower priority.
Alphabetical Order
If bookings have the same state, start time, and priority, a deterministic resolution is achieved through an alphabetical comparison of booking names. Bookings with names that come later alphabetically will have a lower priority.
Note
- A booking that is being created or added is also considered for quarantining.
- Bookings that are already ongoing can also be moved to quarantine.
Dealing with different quarantine reasons
Quarantine on booking updates
When the adding or updating of a booking causes bookings to go to quarantine, errors in the TraceData will indicate that quarantine is needed to solve conflicts. The added or updated bookings will only be saved if the forceQuarantine parameter is set to true.
The error in the TraceData will be of type ReservationUpdateCausedReservationsToGoToQuarantine, and the property MustBeMovedToQuarantine will contain all the bookings and their usage that must be moved to quarantine in order to solve the scheduling conflict. The bookings that will be moved to quarantine will be selected according to their priority (see Quarantine priority).
If the forceQuarantine flag is passed, no error will be returned. Instead a warning of type ReservationInstancesMovedToQuarantine will be present in the TraceData, and the SubjectIds property of the warning will contain the IDs of the bookings that have been moved to quarantine.
The code snippet below shows an example of how this error in the TraceData can be used to retrieve information about the scheduling conflict.
// Create a new ResourceManagerHelper
var helper = new ResourceManagerHelper(engine.SendSLNetSingleResponseMessage);
// Save a 'ReservationInstance' without forcing quarantine
helper.AddOrUpdateReservationInstances(forceQuarantine: false, reservation);
var traceData = helper.GetTraceDataLastCall();
var errors = traceData.GetErrorDataOfType<ResourceManagerErrorData>();
foreach (var error in errors)
{
if (error.ErrorReason != ResourceManagerErrorData.Reason.ReservationUpdateCausedReservationsToGoToQuarantine)
{
// For the sake of example we only handle the quarantine error here, but if there is a different error
// the script should of course not ignore it but handle it appropriately.
continue;
}
var errorBuilder = new StringBuilder("Scheduling conflict. The following bookings need to be moved to quarantine:").AppendLine();
// The bookings that will be moved to quarantine to resolve the conflict are in the 'MustBeMovedToQuarantine' property
foreach (var toQuarantine in error.MustBeMovedToQuarantine)
{
var booking = toQuarantine.ReservationInstance;
errorBuilder.AppendLine($"{booking.Name} ({booking.ID}):");
foreach(var quarantinedUsage in toQuarantine.QuarantinedUsages)
{
var resourceUsage = quarantinedUsage.QuarantinedResourceUsage;
errorBuilder.AppendLine($"\tresource with ID '{resourceUsage.GUID}' will be quarantined because:");
// The 'QuarantineTriggers' contains information about why this usage was moved to quarantine
foreach (var trigger in quarantinedUsage.QuarantineTriggers)
{
errorBuilder.Append($"\t\t{trigger.QuarantineReason}. ");
// From DataMiner 10.5.2/10.6.0 onwards (RN 41399), the 'ReservationConflictType' can provide more detailed information
// when a booking update causes a quarantine.
if (trigger.ReservationConflictType != ReservationConflictReason.None)
{
errorBuilder.Append($"Conflict reason: {trigger.ReservationConflictType}");
}
errorBuilder.AppendLine();
}
}
}
// Example value of 'errorBuilder.ToString()':
// Scheduling conflict. The following bookings need to be moved to quarantine::
// Test Booking 1 (54add931-66fc-44f5-a76e-95ad0317f6af):
// resource with ID 'a250cffb-7054-4704-aa58-96200b0c49b3' will be quarantined because:
// ReservationInstanceUpdated. Conflict reason: ConcurrencyOverflow
}
When a booking is saved with the forceQuarantine flag set to true, there will be warnings about the bookings that have automatically been moved to quarantine.
// Save a 'ReservationInstance' and force quarantine
helper.AddOrUpdateReservationInstances(forceQuarantine: true, reservation);
var traceData = helper.GetTraceDataLastCall();
// When forcing quarantine the call should succeed even if there are conflicts.
// If the traceData does not indicate the call succeeded the error must be handled.
if (!traceData.HasSucceeded())
{
// The script should handle the error here, but in this example we will just return.
return;
}
foreach (var warning in traceData.WarningData)
{
if (!(warning is ResourceManagerWarningData resourceManagerWarning) ||
resourceManagerWarning.WarningReason != ResourceManagerWarningData.Reason.ReservationInstancesMovedToQuarantine)
{
// For the sake of example we only handle the quarantine warning here, but if there is a different warning
// the script should of course not ignore it but handle it appropriately.
continue;
}
var bookingIds = string.Join(", ", resourceManagerWarning.SubjectIds);
var warningString = "The following bookings were moved to quarantine: {bookingIds}";
// Example value of 'warningString':
// The following bookings were moved to quarantine: 54add931-66fc-44f5-a76e-95ad0317f6af, 69958b9b-5704-4532-bb08-b021c5437084
}
Quarantine on resource updates
Quarantine on resource updates works almost the same as quarantine on booking updates. Similar as for booking updates, bookings will only be moved to quarantine if the forceQuarantine flag is passed.
The following updates to resources can trigger quarantine:
- Decreasing the MaxConcurrency of a resource.
- Changing the mode of a resource to Maintenance. This will move all bookings using that resource to quarantine.
- Deleting a capacity or capability. All bookings using the deleted capacity/capability of this resource will be moved to quarantine.
- Decreasing a maximum capacity in such a way that existing bookings are no longer supported.
- Changing or removing a capability in such a way that currently booked values are no longer supported.
- Changing the availability window in such a way that existing bookings are no longer supported (see Resource availability).
Note
Deletion of a resource will not trigger quarantine, but this will always be blocked if the resource is in use in a future or ongoing booking.
If a quarantine conflict arises when a resource is updated and the call is not forced, the returned error in the TraceData will be of type ResourceUpdateCausedReservationsToGoToQuarantine.
// Create a new ResourceManagerHelper
var helper = new ResourceManagerHelper(engine.SendSLNetSingleResponseMessage);
helper.AddOrUpdateResources(forceQuarantine: false, resource);
var traceData = helper.GetTraceDataLastCall();
var errors = traceData.GetErrorDataOfType<ResourceManagerErrorData>();
foreach (var error in errors)
{
if (error.ErrorReason != ResourceManagerErrorData.Reason.ResourceUpdateCausedReservationsToGoToQuarantine)
{
// For the sake of example we only handle the quarantine error here, but if there is a different error
// the script should of course not ignore it but handle it appropriately.
continue;
}
var conflictInformation = error.ConflictInformation;
var errorBuilder = new StringBuilder($"Scheduling conflict. The following bookings need to be moved to quarantine:").AppendLine();
// The bookings that will be moved to quarantine are in the 'ConflictingUsages' property
foreach (var toQuarantine in conflictInformation.ConflictingUsages)
{
var booking = toQuarantine.Instance;
errorBuilder.AppendLine($"{booking.Name} ({booking.ID}):");
var usageToQuarantine = toQuarantine.Usage;
errorBuilder.AppendLine($"\tresource with ID '{usageToQuarantine.GUID}' will be quarantined because:");
// The 'QuarantineTriggers' contains information about why this usage was moved to quarantine
foreach (var trigger in toQuarantine.Triggers)
{
errorBuilder.Append($"\t\t{trigger.QuarantineReason}");
errorBuilder.AppendLine();
}
}
// Example value of 'errorBuilder.ToString()' when a booking is moved to quarantine because we decreased the 'MaxConcurrency' property of a resource:
// Scheduling conflict. The following bookings need to be moved to quarantine::
// Test Booking 1 (54add931-66fc-44f5-a76e-95ad0317f6af):
// resource with ID 'a250cffb-7054-4704-aa58-96200b0c49b3' will be quarantined because:
// ConcurrencyDowngraded
}
Saving a resource with the forceQuarantine flag set to true will return a warning of type ReservationInstancesMovedToQuarantine in the TraceData. Under Quarantine on booking updates, you can find an example script showing how to retrieve that information.
Quarantine on interrupted contributing bookings
When Resource Manager starts up, the bookings in the database will be checked to see if they should have started or stopped or had an event run while Resource Manager was not running. If any such bookings are found, they will be put in the Interrupted state. If a contributing booking is moved to the Interrupted state, the bookings making use of the corresponding contributing resource will be moved to the quarantine state. The QuarantineTrigger will have the value ContributingResourceNotAvailable for the QuarantineReason field in that case.
Overview of possible QuarantineReason values
The script examples above show how the quarantine-related errors in the TraceData can be used to retrieve information about the scheduling conflict. Each quarantined ResourceUsageDefinition will have a QuarantineTrigger with a QuarantineReason to keep track of why a usage was moved to quarantine.
These are the possible values for the QuarantineReason field:
| QuarantineReason value | Used when |
|---|---|
| CapacityDeleted | A capacity was completely removed from a resource. |
| CapabilityDeleted | A capability was completely removed from a resource. |
| CapacityDowngraded | A capacity was downgraded on a resource, meaning that the maximum capacity value was lowered. |
| CapabilityDowngraded | A capability was downgraded on a resource. This could be a range point capability where the min-max range was narrowed, or a discrete capability where a discrete value was removed. |
| ConcurrencyDowngraded | The maximum concurrency of a resource was lowered. |
| MovedToMaintenance | The resource was moved to the Maintenance state. |
| ReservationInstanceUpdated | A booking was added or updated and caused a scheduling conflict. |
| ContributingResourceNotAvailable | A contributing resource is not available. This can happen when contributing bookings are interrupted, or when trying to assign an unavailable contributing resource to a booking. |
| ResourceAvailabilityWindowChanged | The availability of a resource changed. This can happen when the availability window resource is updated in such a way that existing bookings fall outside of the availability. See Resource availability. |
Overview of possible ReservationConflictType values
The script example for Quarantine on booking updates shows that from DataMiner 10.5.2/10.6.0 onwards, the QuarantineTrigger will have a ReservationConflictType field if the conflict was caused by a booking update. The table below shows the possible values for the ReservationConflictType field.
| ReservationConflictType value | Reason |
|---|---|
| ConcurrencyOverflow | The resource does not have enough concurrency to support all bookings. |
| CapacityOverflow | The booked resource does not have enough capacity to support all bookings. |
| UnavailableCapability | The booked resource does not provide the requested capability value. |
| UnavailableTimeDependentCapability | The booked time-dependent capability on the resource has a conflict with a different booking. |
| OutsideResourceAvailabilityWindow | The resource has an availability window defined and is not available in the time range of the booking. See also Resource availability. |
Moving bookings out of the quarantine state
Note
The SRM framework provides a feature to recover bookings from the quarantine state. By default, this will trigger the SRM_LeaveQuarantineState script, but this can be customized. See using custom scripts.
To resolve the quarantine state, you can inspect the quarantined usage of a booking, and you can either restore it or assign a new resource.
The script example below will show how to restore resources that were put in quarantine. This approach will only work if the bookings that caused the conflict have been updated so the resources are available again for the quarantined booking.
var helper = new ResourceManagerHelper(engine.SendSLNetSingleResponseMessage);
// All bookings in the quarantine state can be retrieved with a filter.
// An extra filter is added here to only retrieve quarantined bookings that need to start in the next 7 days.
var filter = ReservationInstanceExposers.IsQuarantined.Equal(true)
.AND(ReservationInstanceExposers.End.GreaterThan(DateTime.UtcNow))
.AND(ReservationInstanceExposers.Start.LessThan(DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(7)));
var quarantinedBookings = helper.GetReservationInstances(filter);
foreach (var booking in quarantinedBookings)
{
// Create a dictionary of the usage that still exists on the booking and its quarantine reference.
var existingUsagesWithQuarantineReference = booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance
.Where(r => r.QuarantineReference != Guid.Empty)
.ToDictionary(r => r.QuarantineReference);
foreach (var quarantinedResource in booking.QuarantinedResources)
{
var quarantinedUsageDefinition = quarantinedResource.QuarantinedResourceUsage;
// The quarantinedResource contains a list of triggers which keep track of when and why a usage was moved to quarantine.
// The script will log these for the sake of example.
var logBuilder = new StringBuilder();
logBuilder.AppendLine($"Resource with ID '{quarantinedUsageDefinition.GUID}' was moved to quarantine for the following reasons:");
foreach (var oneTrigger in quarantinedResource.QuarantineTriggers)
{
logBuilder.AppendLine($"\tat {oneTrigger.CreatedAt:dd/mm/yyyy HH:mm.ss} because {oneTrigger}");
}
// Example value of 'logBuilder.ToString()':
// Resource with ID 'dda81819-58a2-4f52-8812-8ac823f2842d' was moved to quarantine for the following reasons:
// at 26/09/2024 08:09.26 because ReservationInstanceUpdated: b0c1522d-de1d-4597-b48e-b6f0279135ed
if (existingUsagesWithQuarantineReference.TryGetValue(quarantinedUsageDefinition.QuarantineReference, out var existingUsage))
{
// This quarantined usage was split off and some usage is still assigned to the booking.
// This usually happens when there is a capacity overflow and some capacity is still assigned to the resource.
// Merge the existing usage with the old usage to restore the resource usage.
// If the goal of the script is to assign a completely new resource to resolve the quarantine state, the 'existingUsage'
// should be removed from the 'ResourcesInReservationInstance' collection.
if (quarantinedUsageDefinition.RequiredCapabilities.Count > 0)
{
existingUsage.RequiredCapabilities.AddRange(quarantinedUsageDefinition.RequiredCapabilities);
}
foreach (var requiredCapacity in quarantinedUsageDefinition.RequiredCapacities)
{
var currentCapacity = existingUsage.RequiredCapacities.SingleOrDefault(x => x.CapacityProfileID == requiredCapacity.CapacityProfileID);
if (currentCapacity != null)
{
currentCapacity.DecimalQuantity += requiredCapacity.DecimalQuantity;
}
else
{
existingUsage.RequiredCapacities.Add(requiredCapacity);
}
}
existingUsage.QuarantineReference = Guid.Empty;
}
else
{
// The entire usage is in quarantine, nothing is assigned to the booking anymore for this resource.
quarantinedResource.QuarantinedResourceUsage.QuarantineReference = Guid.Empty;
// Re-assign the old resource usage
booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance.Add(quarantinedResource.QuarantinedResourceUsage);
}
}
booking.QuarantinedResources.Clear();
// 'FindBookingManager' and 'RemoveFromQuarantine' is an extension method provided by the SRM framework
var bookingManager = booking.FindBookingManager();
helper.RemoveFromQuarantine(booking, bookingManager);
}
In order to select a new resource, some code will need to be written to select this new resource according to some criteria. Below is a simple example script that shows how to select a new resource based of the result of a GetEligibleResources call:
...
var contexts = new List<EligibleResourceContext>();
var contextIdsToUsages = new Dictionary<Guid, ResourceUsageDefinition>();
foreach (var booking in quarantinedBookings)
{
// Create a dictionary of the usage that still exists on the booking and its quarantine reference.
var existingUsagesWithQuarantineReference = booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance
.Where(r => r.QuarantineReference != Guid.Empty)
.ToDictionary(r => r.QuarantineReference);
foreach (var quarantinedResource in booking.QuarantinedResources)
{
ResourceUsageDefinition usage = null;
// If there is still existing usage, we need to merge the required capacities and capabilities
if (existingUsagesWithQuarantineReference.TryGetValue(usage.QuarantineReference, out var stillBooked))
{
usage = stillBooked;
var quarantinedUsage = quarantinedResource.QuarantinedResourceUsage;
foreach (var quarantinedCapacity in quarantinedUsage.RequiredCapacities)
{
var alreadyInUsage = usage.RequiredCapacities.FirstOrDefault(r => r.CapacityProfileID == quarantinedCapacity.CapacityProfileID);
if (alreadyInUsage != null)
{
alreadyInUsage.DecimalQuantity += quarantinedCapacity.DecimalQuantity;
}
else
{
usage.RequiredCapacities.Add(quarantinedCapacity);
}
}
foreach (var quarantinedCapability in quarantinedUsage.RequiredCapabilities)
{
// Capabilities are moved completely so they can copied over
usage.RequiredCapabilities.Add(quarantinedCapability);
}
}
else
{
usage = quarantinedResource.QuarantinedResourceUsage;
}
// This will get all resources that are available with the capacities and capabilities that were
// originally required.
var context = new EligibleResourceContext(booking.TimeRange)
{
RequiredCapacities = usage.RequiredCapacities,
RequiredCapabilities = usage.RequiredCapabilities
};
contextIdsToUsages[context.ContextId] = usage;
// If only resources that match a certain filter should be considered this extra filter can be added to the context.
// For example to only consider resources that are part of a certain pool:
// var poolId = resourcePool.ID;
// context.ResourceFilter = ResourceExposers.PoolGUIDs.Contains(poolId);
contexts.Add(context);
}
var results = helper.GetEligibleResources(contexts);
var usages = new List<ResourceUsageDefinition>();
string error = "";
foreach (var eligibleResourceResult in results)
{
if (eligibleResourceResult.EligibleResources.Count == 0)
{
var context = contexts.First(c => c.ContextId == eligibleResourceResult.ForContextId);
error += $"Could not find a resource with filter: {context}{Environment.NewLine}";
continue;
}
// Overwrite the resource on the usage with the first eligible resource.
var usage = contextIdsToUsages[eligibleResourceResult.ForContextId];
usage.GUID = eligibleResourceResult.EligibleResources[0].ID;
usages.Add(usage);
}
if (error != string.Empty)
{
// The error should of course be handled but this example script will just return.
return;
}
booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance.RemoveAll(r => r.QuarantineReference != Guid.Empty);
foreach (var usage in usages)
{
usage.QuarantineReference = Guid.Empty;
booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance.Add(usage);
}
booking.QuarantinedResources.Clear();
// 'FindBookingManager' and 'RemoveFromQuarantine' is an extension method provided by the SRM framework
var bookingManager = booking.FindBookingManager();
helper.RemoveFromQuarantine(booking, bookingManager);
}