Checking the required open ports in a DMS
The procedure below allows you to check if communication using specific ports is possible in a DataMiner System. This can for instance be useful to check if there are any firewall issues when you prepare for an upgrade to a recent DataMiner version.
Requirements
- Access to the server with administrator rights. This requires a connection dedicated completely or partially to this procedure, via VPN or local network.
- PowerShell and PowerShell ISE on all DMAs.
Procedure
Check the requirements and connection
Prerequisites
- Remote access to all DMAs in the system.
- User credentials with administrator rights.
- PowerShell and PowerShell ISE are available on all DMAs in the system.
Steps
- Connect to the system via the designated VPN or host PC. Check the remote access to each DMA.
- Check if PowerShell and PowerShell ISE are available.
Check the ports
Prerequisites
All previous requirements are met.
Steps
For an overview of the ports that are required for DataMiner communication, see Overview of IP ports used in a DMS. Follow the steps below to check these ports for each DMA.
Connect to each DMA you need to check, and use the following PowerShell command to enable a port for listening on a server:
powershell.exe -Command {$x = [System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener]<PORT>; $x.Start(); Start-Sleep -Seconds <TIME IN SECONDS>}You can for example use the following command to open port 9090 for listening for 8 hours (28800 seconds), so that the port remains open for the duration of the test until it is closed:
powershell.exe -Command {$x = [System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener]9090; $x.Start(); Start-Sleep -Seconds 28800}Open a separate PowerShell or PowerShell ISE instance for each port you want to check.
To start running the command, click the Run button (or press F5), or select the desired row and click the Run Selection button (or press F8). To stop running the command, click Stop Operation (or press Ctrl+C).
Open another PowerShell ISE instance to check the open ports on each DMA. Use the following command to test connectivity to a socket:
Test-NetConnection <DMA IP> -port <PORT>For example, in case you are connected to a DMA with IP 100.0.0.1 and also need to check two other DMAs with IP 100.0.0.2 and 100.0.0.3 respectively, you can use the following script to test ports 9090, 4222, 6222 and 8222:
Test-NetConnection localhost -port 9090 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.2 -port 9090 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.3 -port 9090 Test-NetConnection localhost -port 4222 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.2 -port 4222 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.3 -port 4222 Test-NetConnection localhost -port 6222 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.2 -port 6222 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.3 -port 6222 Test-NetConnection localhost -port 8222 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.2 -port 8222 Test-NetConnection 100.0.0.3 -port 8222Once you have all port listeners running on all DMAs, you can test all ports at once on each server. To do so, select all commands in the command window, and run them all by clicking Run Selection (or pressing F8) or clicking Run (or pressing F5). For failed connections "False" will be displayed, while for successful connections "True" will be displayed.
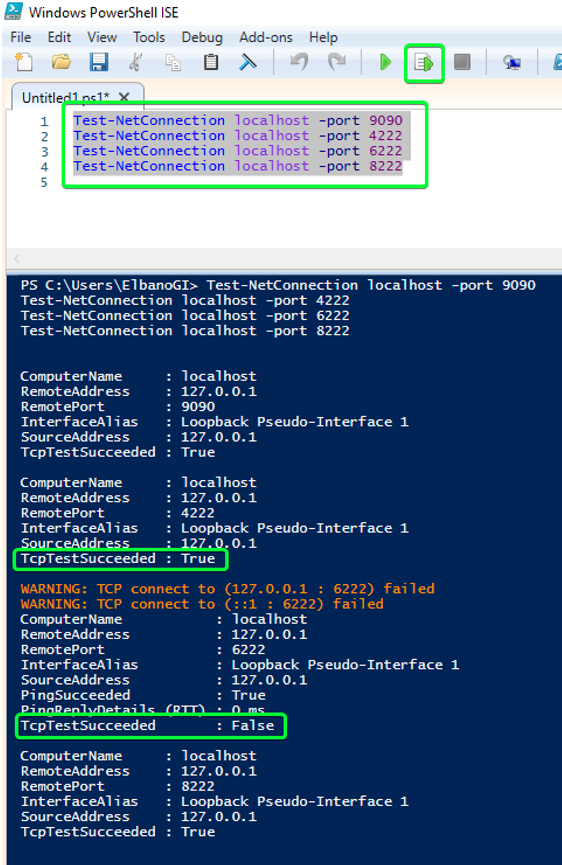
Example of 4 ports being tested on a local DMA
Time estimate
| Item | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Checking the requirements | ~30 min. (depending on the number of DMAs) |
| 2 | Checking the ports | ~60 min. (depending on the number of DMAs) |