Replacing a dead Cassandra node (Linux)
This article describes how you can replace a non-functioning or "dead" Cassandra node running on a Linux system. It is applicable for Cassandra versions 3.7 and 3.11 at the time of writing.
Please make sure to validate the required steps with those provided by the Apache Cassandra team. See the official documentation for Apache Cassandra.
Requirements
- Basic Cassandra knowledge
- Access to the Cassandra cluster infrastructure
- Server administrator rights
- DataMiner administrator rights
Procedure
Install a new blank Cassandra node
Deploy and install a new blank Cassandra node in the network.
It is important to start from a new blank Cassandra installation to prevent any conflicts.
Update the existing Cassandra nodes
If the dead Cassandra node was a seed node, change the cluster's seed node configuration on each node.
To do so, in the cassandra.yaml file of each node, replace the IP address of the dead node from the seeds list with the IP address of the new node.
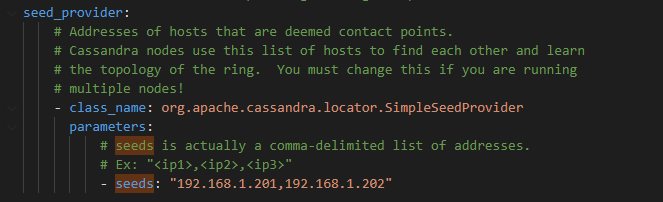
Example of seeds list in Cassandra.yaml file
After you have updated the configuration, restart the Cassandra service:
Stop the Cassandra service, using the following command:
sudo service cassandra stopFind the Cassandra java process ID and then kill the process using its PID. Use the following commands:
ps auwx | grep cassandra sudo kill {PID}Start the Cassandra service, using the following command:
sudo service cassandra start
Update the new node
Stop the Cassandra service on the new node, using the following command:
sudo service cassandra stopFind the Cassandra java process ID and then kill the process using its PID. Use the following commands:
ps auwx | grep cassandra sudo kill {PID}Clear all data from the new node, using the following commands:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/cassandra/* sudo rm /etc/cassandra/cassandra-topology.propertiesIn the Cassandra.yaml configuration file, update the following fields:
- Cluster_name: Must be set to the same value as other nodes in the cluster. Example:
cluster_name: 'DMS' - Listen_addres: The server host IP. Example:
listen_address: 192.168.1.204 - RPC_Address: The server host IP. Example:
rpc_address: 192.168.1.204 - Seed list: Must be set to the same value as is configured on the other nodes in the cluster. Example:
seeds: "192.168.1.201,192.168.1.202" - auto_bootstrap: If this setting exists and is set to false, set it to true:
auto_bootstrap: true
- Cluster_name: Must be set to the same value as other nodes in the cluster. Example:
Start the new node with the replace_address option
On the new node, edit the Cassandra-env.sh file and add the following:
JVM_OPTS="$JVM_OPTS -Dcassandra.replace_address_first_boot={ip of dead node}"
For example:
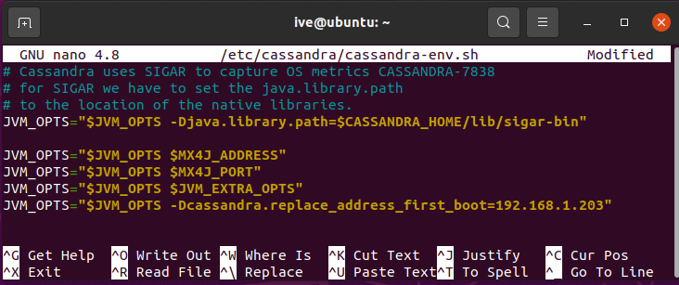
When this is done, start the Cassandra service, using the following command:
sudo service cassandra start
Check whether the new node remains in the DN state until bootstrapping is completed. You can check progress using the following command:
nodetool netstats
Confirm that the new node has replaced the dead node using the following command:
nodetool status
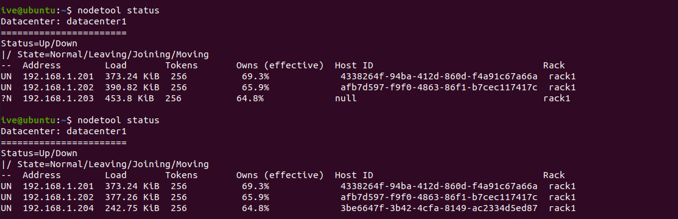
After the node bootstraps, remove the replace-address parameter from the Cassandra-env.sh file.
Run a repair
This step is only necessary if the node has been down for longer than the time configured for the max_hint_window_in_ms setting in the cassandra.yaml file. By default, this is 3 hours.
In this case, use nodetool to run a repair. For more information, see https://cassandra.apache.org/doc/latest/tools/nodetool/repair.html.
Update DataMiner
In DataMiner Cube, go to System Center > Database. In the DB server box, replace the IP address of the dead node with the IP address of the new node.
For example, in DataMiner 10.2.0:
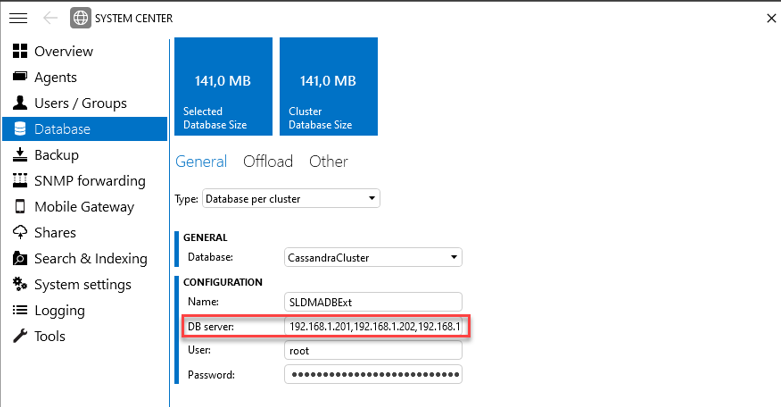
Time estimate
| Item | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Installing a new blank node | 30 min. |
| 2 | Updating the existing nodes | 5 – 10 min. |
| 3 | Updating the new node | 5 min. |
| 4 | Starting the new node with the replace_address option | a few minutes to multiple hours, depending on the size of the dataset |
| 5 | Running a repair (only if node was down longer than max_hint_window_in_ms) | a few minutes to multiple hours, depending on the size of the dataset |
| 6 | Updating DataMiner | 1 min. |