Resources benchmarks
Resource performance
Below you can find the results of performance testing for resource add, update, and delete operations. The test setup used a local Elasticsearch database. Elasticsearch started to outperform XML storage when more than 2000 resources were present in the system.
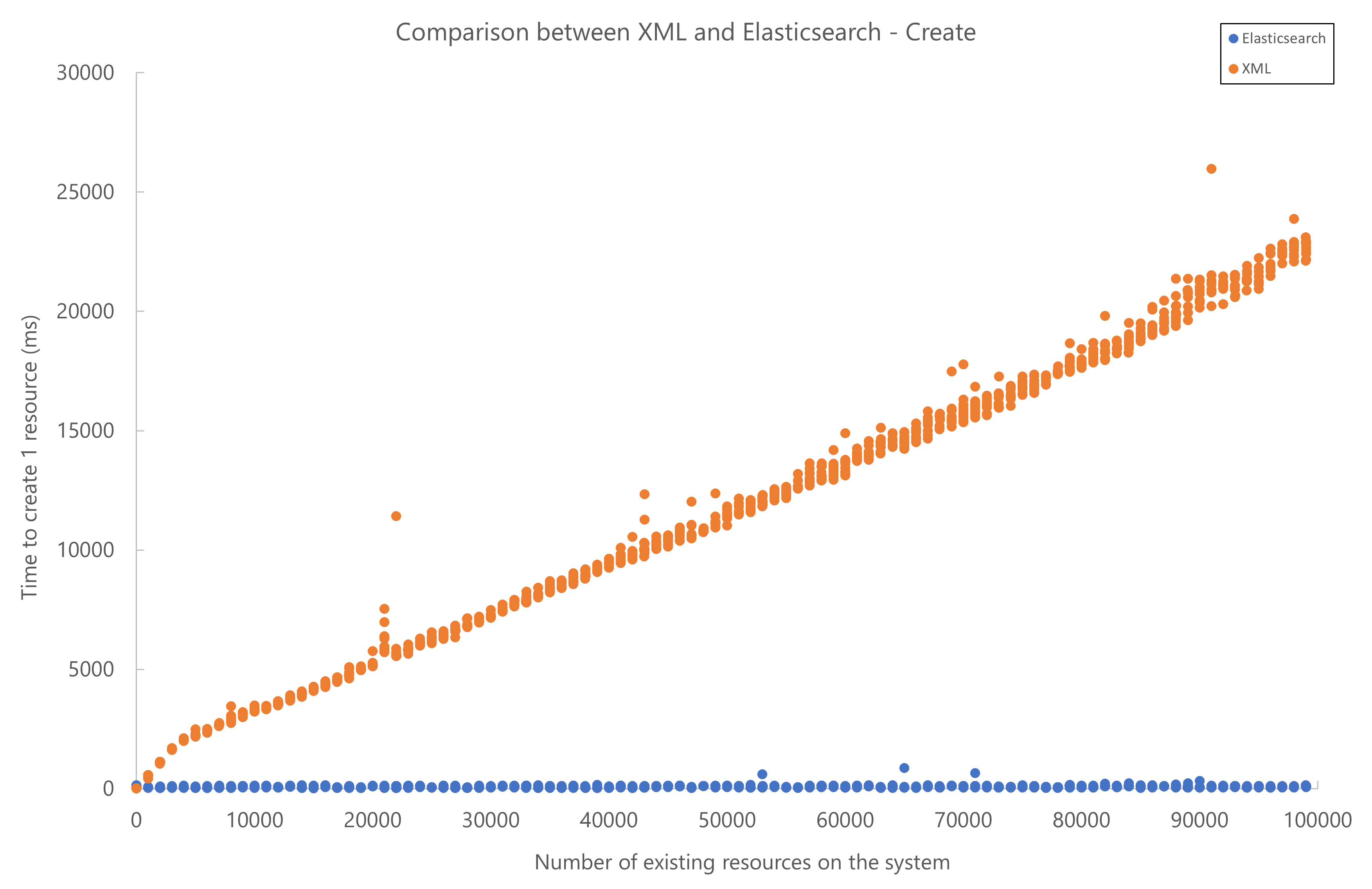
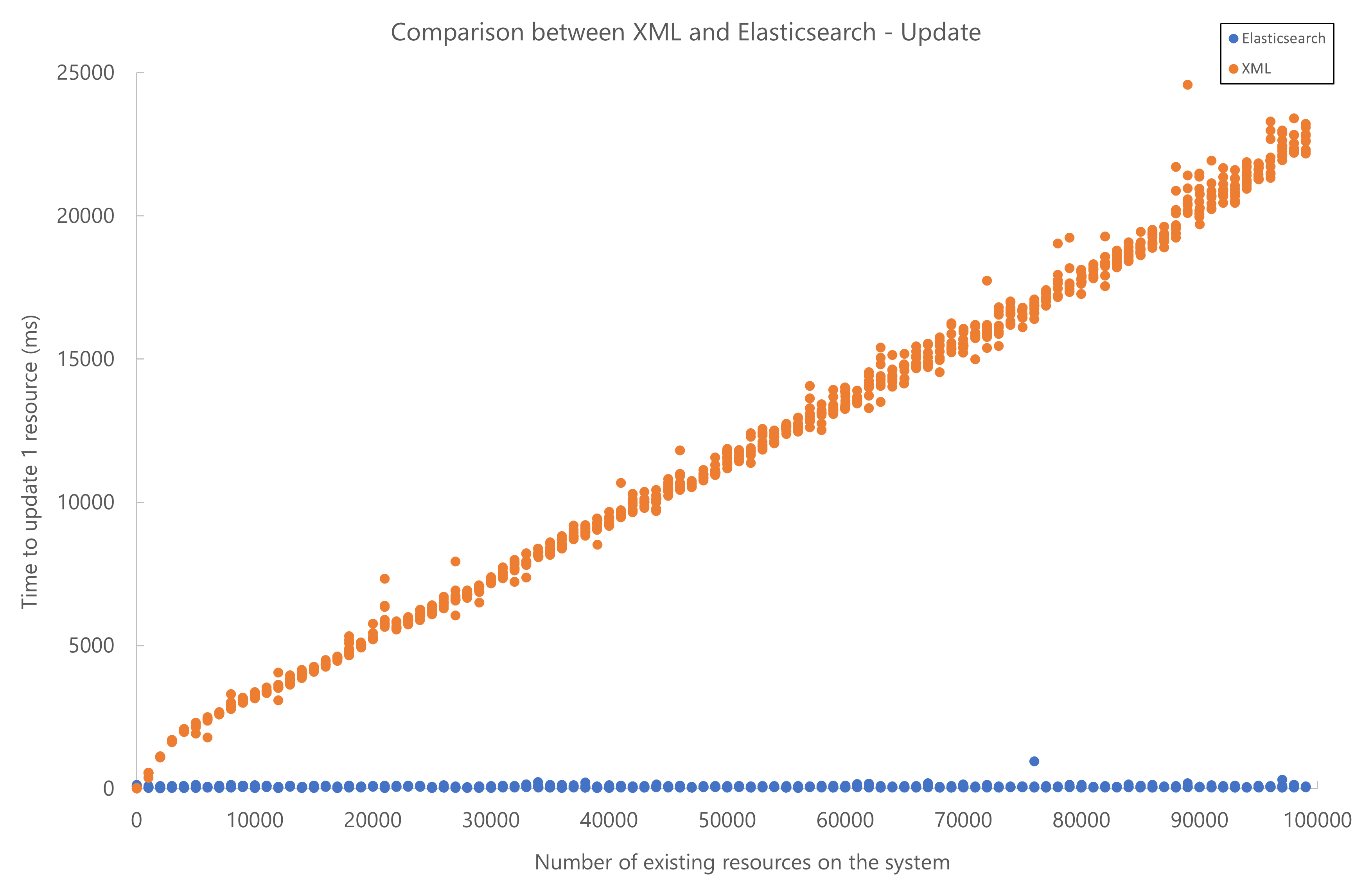
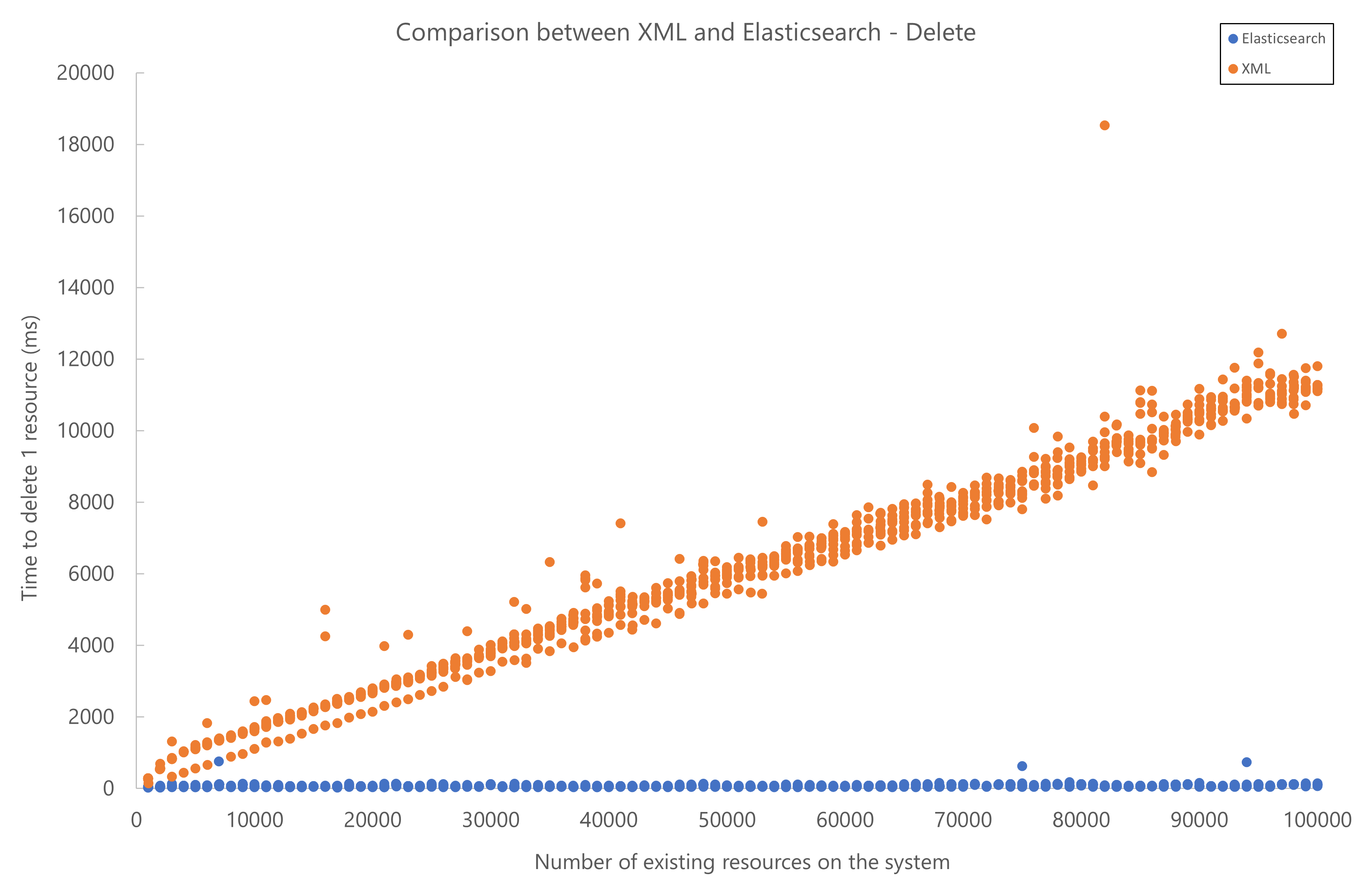
Note
Read performance of resources and resource pools is the same for XML and Elasticsearch storage, since all reads will go to a cache in SLNet.
Resource Manager startup performance
Below you can find the startup time for Resource Manager with a large number of resources using XML storage and using Elasticsearch storage:
| Storage type | Resource cache load time | ResourceManager startup time |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticsearch | 34s | 1m 45s |
| Xml | 47s | 1m 52s |
The Resource cache load time column shows the time it takes for Resource Manager to load all resources in its cache on startup.
The ResourceManager startup time is the total time until Resource Manager is operational after initial startup. This includes the time it takes to initialize all storage types. This can be higher if a lot of bookings are currently active or will start soon. It does not include the time Resource Manager spends syncing with other DataMiner Agents in the cluster if XML storage is used. Resource Manager is considered operational before it has fully synced, as it can start handling API requests.