Retrieving tables
Tables in a MIB are structured as illustrated below. There is always a table folder, followed by an entry folder containing the column parameters.
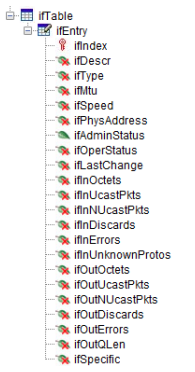
In a protocol, a table is implemented using a parameter representing the table (of type "array") and additional parameters for each column in the table. By adding <SNMP> tags that include the appropriate <OID> definitions, you can map the table and its columns to the corresponding SNMP table and column OIDs, enabling SNMP polling similar to polling single variables.
Retrieval methods
A protocol can retrieve SNMP tables using various methods. The desired method is specified on the table parameter by setting the options attribute within the
GetNext: Fetches each cell individually using SNMP GetNext requests.
GetNext + MultipleGet (column-based): Uses GetNext requests to fetch the instance identifier of each row individually. Then, Get requests are used to fetch multiple cells at once, proceeding column by column, only moving to the next column when all cells have been fetched.
GetNext + MultipleGet (row-based): Uses GetNext requests to fetch the instance identifier of each row individually. Then, Get requests are used to fetch all column values for multiple rows at a time.
MultipleGetNext: Uses GetNext requests to fetch all column values for one row at a time.
MultipleGetBulk: Uses GetBulk requests to fetch all column values for multiple rows at a time.
Note
The Protocol Development Guide Companion Files include the following Wireshark captures to help understand the different retrieval methods:
- GetNext.pcap
- GetNext+MultipleGet.pcap
- MultipleGetNext.pcap
- MultipleGetBulk.pcap
- MultipleGetBulkMaxRep2.pcap.
- Additionally, the companion files also include example protocols for each table retrieval method.
An example protocol "SLC SDF SNMP - Tables" is also available in the companion files.
Differences between Get, GetNext, and GetBulk
It can be helpful to understand the differences between the three main SNMP operations used to retrieve data:
Get requests retrieve the values of specific OIDs. They require you to know the exact OIDs you want to retrieve.
GetNext requests retrieve the next OID in the MIB tree. This makes them ideal for walking through tables or discovering unknown entries, but they can be less efficient and harder to control.
GetBulk requests were introduced in SNMPv2 as a more efficient GetNext. Next to the requested OIDs as usual, these also includes two new parameters:
- non-repeaters: The number of OIDs that only need to be retrieved once.
- max-repetitions: The number of times to repeat retrieval for the remaining OIDs.
This enables the agent to effectively repeat the equivalent of multiple subsequent GetNext requests in a single response. This reduces the number of round trips required, making it especially efficient for retrieving rows from SNMP tables.
Tips for selecting a retrieval method
In general, the more messages required to retrieve a table, the longer the process will take. To optimize performance and compatibility, and to minimize the risk of index shift issues, follow this advice when selecting a retrieval method:
Start with MultipleGetBulk, as it typically offers the best performance.
If the device does not support SNMPv2, fall back to MultipleGetNext. DataMiner does this automatically if the element is configured for SNMPv1.
If the device cannot handle MultipleGetNext because of memory or processing limitations, try GetNext + MultipleGet (column-based).
If issues persist, reduce the number of cells to retrieve to lessen the burden on the device.
Avoid using GetNext to prevent poor performance and because of the reduced freedom to select which columns to poll.
Choose GetNext + MultipleGet (row-based) over GetNext + MultipleGet (column-based) when using the subtable feature.
GetNext
This retrieval method fetches each cell individually using SNMP GetNext requests.
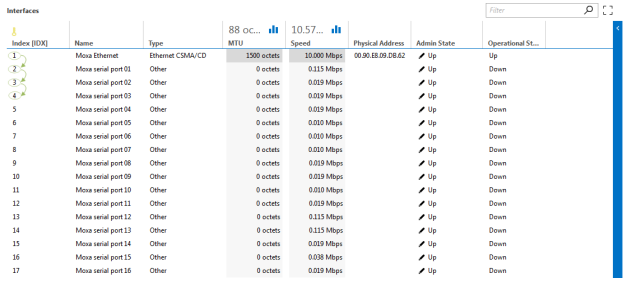
With the GetNext method, you cannot explicitly select which columns to poll by specifying column OIDs. Only the table OID is used, and any OIDs defined on column parameters will be ignored. You can define a protocol table with fewer columns than exist in the SNMP table, but the columns must be defined in a continuous, ordered sequence starting from the first column. Skipping columns or defining them out of order is not supported. For example, if the SNMP table has eight columns, you may define only the first three, but you cannot define just the first and third columns while omitting the second.
Note
From DataMiner 10.4.0 [CU10]/10.5.0 [CU0]/10.5.1 onwards, GetNext only retrieves the columns defined in your protocol table. In earlier DataMiner versions, all columns are polled, but only defined columns are displayed.
Important
When using the GetNext method, you must specify the table OID on the table parameter. Do not specify OIDs on the column parameters, as these will be ignored.
Caution
This method is vulnerable to the index shift issue.
Example
<Param id="1000">
<Name>Interfaces</Name>
<Description>Interfaces</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1001" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1002" type="snmp" />
...
</ArrayOptions>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2</OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1001" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesIndex</Name>
<Description>Instance (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
</Param>
<Param id="1002" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesName</Name>
<Description>Name (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
</Param>
SNMP communication flow:
The initial request is an SNMP GetNext request with the OID of ifEntry (1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1). This returns the content of 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1 (first row, first column).
Prior to DataMiner 10.4.0 [CU10]/10.5.0 [CU0]/10.5.1, additional GetNext requests are performed until the OID in the response exceeds the table OID range. From DataMiner 10.4.0 [CU10]/10.5.0 [CU0]/10.5.1 onwards, GetNext requests are performed until the values of the defined column parameters are retrieved or, in case the number of defined columns exceeds the number of column values, until the table OID range is exceeded.
GetNext + MultipleGet (column-based)
This retrieval method uses GetNext requests to fetch the index of each row individually. Then, Get requests are used to fetch multiple cells at once, proceeding column by column, only moving to the next column when all cells have been fetched. If the configured size is large enough, multiple columns (or part of the next column) can be included in a single request.
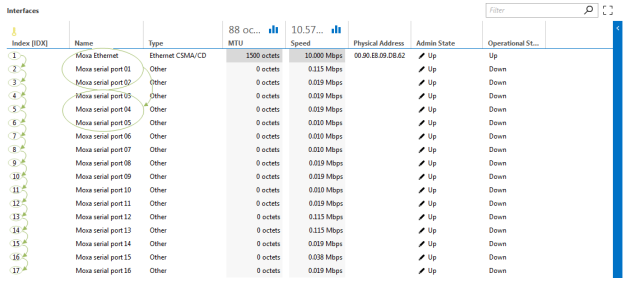
To use this polling method, add bulk to the options attribute of the table parameter's OID tag. You can specify the number of cells to retrieve per request by adding a value after bulk (e.g., bulk:10). If no value is provided, the default is 50.
Caution
This method is vulnerable to the index shift issue.
Example
<Param id="1000">
<Name>Interfaces</Name>
<Description>Interfaces</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1001" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1002" type="snmp" />
...
</ArrayOptions>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" options=";bulk:3"></OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1001" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesIndex</Name>
<Description>Instance (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1</OID>
<Type>Integer32</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1002" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesName</Name>
<Description>Name (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2</OID>
<Type>octetstring</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
SNMP communication flow:
GetNext requests are performed to fetch the instance identifiers of all rows, starting with the OID of ifEntry (1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1).
Once all row instance identifiers are known, Get requests are performed to fetch all table cells in column order. Each request includes multiple variable bindings, with the number of values per request determined by the bulk size. If the bulk size is smaller than the column, multiple requests are needed to fetch all values for that column. Only the SNMP columns defined in the table parameter are fetched.
GetNext + MultipleGet (row-based)
This retrieval method uses GetNext requests to fetch the index of each row individually. Then, Get requests are used to fetch all columns for one or multiple rows at once.
To use this polling method, add multipleGet to the options attribute of the table parameter's OID tag. You can specify the number of rows to retrieve per request by adding a value after multipleGet (e.g., multipleGet:10). If no value is provided, the default is 10.
Example
<Param id="1000">
<Name>Interfaces</Name>
<Description>Interfaces</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1001" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1002" type="snmp" />
...
</ArrayOptions>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" options=";multipleGet:3"></OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1001" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesIndex</Name>
<Description>Instance (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1</OID>
<Type>Integer32</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1002" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesName</Name>
<Description>Name (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2</OID>
<Type>octetstring</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
SNMP communication flow:
GetNext requests are performed to fetch the instance identifiers of all rows, starting with the OID of ifEntry (1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1).
Once all row instance identifiers are known, Get requests are performed to fetch all table cells. Each request includes multiple variable bindings that contain all SNMP columns defined in the table parameter, with the number of rows per request determined by the bulk size.
MultipleGetNext
This retrieval method uses GetNext requests to fetch all column values for one row at a time.
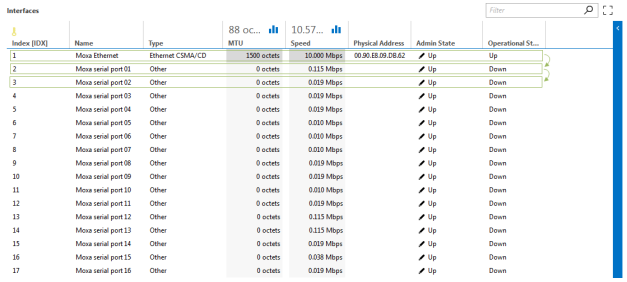
To use this polling method, add multipleGetNext to the options attribute of the table parameter's OID tag.
Example
<Param id="1000">
<Name>Interfaces</Name>
<Description>Interfaces</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1001" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1002" type="snmp" />
...
</ArrayOptions>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" options=";multipleGetNext"></OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1001" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesIndex</Name>
<Description>Instance (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1</OID>
<Type>Integer32</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1002" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesName</Name>
<Description>Name (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2</OID>
<Type>octetstring</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
SNMP communication flow:
A GetNext request is performed to fetch the first row. The request variable bindings contain each column OID defined in the table (e.g., 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1, 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2, etc.).
Then, a GetNext request is sent using the previously retrieved OIDs (e.g., 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.1, 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2.1, etc.).
The GetNext requests proceed until the response contains an OID outside the table range or contains a column OID that is not defined in the protocol table.
MultipleGetBulk
This retrieval method uses GetBulk requests to fetch all column values for multiple rows at a time.
To use this polling method, add multipleGetBulk to the options attribute of the table parameter's OID tag. You can specify the number of rows to retrieve per request by adding a value after multipleGetBulk (e.g., multipleGetBulk:10). If no value is provided, the default is 10.
Note
- Choose the number of rows per request carefully to avoid SNMP responses that exceed the network Path MTU. Large responses may be fragmented, which can reduce reliability. For typical Ethernet networks, keep SNMP responses under 1472 bytes (plus 8 bytes for the UDP header and 20 bytes for the IPv4 header, totaling 1500 bytes). For more details, see RFC 3416, section 2.3.
- The GetBulk request is only available in SNMPv2 and later. This method is not supported on SNMPv1 devices.
Example
<Param id="1000">
<Name>Interfaces</Name>
<Description>Interfaces</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1001" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1002" type="snmp" />
...
</ArrayOptions>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" options=";multipleGetBulk:3"></OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1001" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesIndex</Name>
<Description>Instance (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1</OID>
<Type>Integer32</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1002" trending="false">
<Name>InterfacesName</Name>
<Description>Name (Interfaces)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2</OID>
<Type>octetstring</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>
SNMP communication flow:
A GetBulk request is performed to fetch the first couple of rows. The request variable bindings contain each column OID defined in the table (e.g., 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1, 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2, etc.). The max-repetitions field of the request indicates how many rows will be retrieved.
Then, similar to the GetNext flow, a GetBulk request is sent using the OID of the last row of the previously retrieved OIDs (1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.10, 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2.10, etc.)
The GetBulk requests proceed until the response contains an OID outside the table range, or contains a column OID that is not defined in the protocol table.
Index shift issues during polling
SNMP table indexes are often based on sequential numbers (e.g., 1, 2, 3, etc.). When a row is added or removed from such a table, the indexes of subsequent rows will shift. If DataMiner is polling the table during this shift, and the polling method does not retrieve an entire row in one operation, this can result in inconsistent data retrieval. Parts of a row may be collected before the shift and others after, causing the final row in DataMiner to contain a mix of values from two different rows, leading to an incorrect representation of the data.
To avoid this issue, choose polling methods that can retrieve complete rows in a single operation such as GetNext + MultipleGet (row-based), MultipleGetNext, and MultipleGetBulk.
Caution
Methods that fetch individual columns across multiple requests, such as GetNext or GetNext + MultipleGet (column-based), are especially vulnerable to this problem.
Note
Tables where the row indexes do not shift when rows are added or removed (e.g., tables with fixed or unique indexes) are not affected by this issue.
Instance Option
In DataMiner, SNMP tables must have a single primary key, which is expected to be the value of the first column.
However, some SNMP tables define multiple index columns, meaning the row instance identifier consists of values from more than one column. Additionally, certain SNMP tables may define an index column from a different table. These tables have the same number of rows and maintain a one-to-one relationship.
To correctly poll these types of tables, you must add the instance option to the table parameter. This instructs DataMiner to write the full row instance identifier into the first column of the table.
Important
Do not specify an OID for the first column when using the instance option. The value will be automatically generated and any configured OID will be ignored.
Caution
When the instance option is used with GetNext + MultipleGet (column-based) or GetNext + MultipleGet (row-based), a known issue causes the instance identifier to be written into the second column of the table as well as the first.
Workaround: Create a dedicated column to store the duplicate instance identifier. This column serves only as a workaround and can be hidden by setting RTDisplay to false.
This extra column must define an OID. The actual value does not matter, but it is common to use the OID of the first column of the SNMP table.
The reason for this requirement is that if any SNMP-type column (except the first when using instance) does not specify an OID, DataMiner will automatically fall back to using the GetNext method, since it is the only method that polls without column OIDs. This fallback can lead to unintended behavior and performance issues.
Example
<Param id="1000">
<Name>Table</Name>
<Description>Table</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1001" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1002" type="snmp" />
</ArrayOptions>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" options="instance;multipleGetNext"></OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1001" trending="false">
<Name>TableInstance</Name>
<Description>Instance (Table)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
</Param>
<Param id="1002" trending="false">
<Name>TableColumn1</Name>
<Description>Column 1 (Table)</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete">1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2</OID>
<Type>octetstring</Type>
</SNMP>
</Param>

Subtable option
The subtable option allows you to retrieve a filtered subset of rows from an SNMP table, based on a specified filter. This can significantly reduce the volume of data transferred, especially when only certain rows are relevant.
To enable this feature, add subtable to the options attribute of the SNMP OID tag on the table parameter (i.e., the parameter of type "array"). The filter itself is defined in the SNMP OID tag using the id attribute to reference a parameter containing the desired filter.
Note
- You can specify multiple filters by separating them with commas in the filter parameter (e.g.,
filter1,filter2). - If you require true request-level filtering, consider using dynamic OIDs with wildcards.
Supported polling methods
The subtable option only works with the following methods:
- GetNext + MultipleGet (row-based) (preferred)
- GetNext + MultipleGet (column-based)
These two methods first retrieve the instance identifiers of each row before fetching the column values, which is necessary for the filtering process to work. Among these, row-based is recommended because of its resilience against index shift issues and because it offers better performance in most scenarios.
Behavior
Using the subtable option will result in the following behavior:
The table is initially walked through to gather all row instance identifiers using GetNext.
Each row instance identifier is evaluated against the configured filter.
Once matching rows are identified, only those are polled using Get requests.
Example
In this example, the parameter with ID 101 holds the filter.
<Param id="1000">
<Name>Table</Name>
<Description>Table</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1001" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1002" type="snmp" />
</ArrayOptions>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" options="subtable;multipleGet" id="101"></OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
Filtered set of rows in table using dynamic OID
Another way to retrieve a filtered set of rows is by defining a dynamic OID on the columns (i.e., defining a wildcard ('*') in the OID itself and referencing the filter with the id attribute). No options need to be defined.
The advantage of this method is that only requests are sent to the device matching the desired rows.
For example, suppose the instances of a table are 1.1; 1.2; 1.3; 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 etc. and a filter of 1 is used, then only the instances that start with 1 will be retrieved. The new instances are then 1, 2 and 3.
In the example below, table 1100 will retrieve a filtered set of rows for the column OID 1.2.3.4.* ,where the asterisk is replaced by the content of parameter with ID 1.
<Param id="1100" trending="false">
<Name>Ports</Name>
<Description>Ports</Description>
<Type>array</Type>
<ArrayOptions index="0">
<ColumnOption idx="0" pid="1101" type="snmp" />
<ColumnOption idx="1" pid="1102" type="snmp" />
</ArrayOptions>
<Information>
<Subtext>This shows Information about the Ports on this Device.</Subtext>
</Information>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" options="instance"></OID>
</SNMP>
</Param>
<Param id="1101" trending="false">
<Name>Port Index</Name>
<Description>Port Index</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Interprete>
<RawType>other</RawType>
<Type>string</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
</Param>
<Param id="1102" trending="false">
<Name>Port Type</Name>
<Description>Port Type</Description>
<Type>read</Type>
<Information>
<Subtext>The type of the port.</Subtext>
</Information>
<SNMP>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<OID type="complete" id="1">1.2.3.4.*</OID>
</SNMP>
<Interprete>
<RawType>numeric text</RawType>
<Type>double</Type>
<LengthType>next param</LengthType>
</Interprete>
...
</Param>