Life cycle of ad hoc data sources
Whenever an ad hoc data source is used, an instance of the associated C# class is created, and GQI will call the relevant life cycle methods that define its behavior.
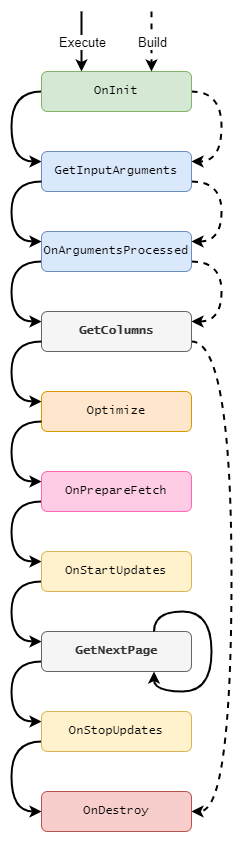
The simplified diagram below shows in what order each GQI life cycle method is called.
Note
In practice, the life cycle methods that will be called depend on various conditions. Refer to the detailed life cycle overview for a complete overview.
When is an ad hoc data source instance created?
A new ad hoc data source instance is created every time one of the following requests occur:
- A capability request, used to determine the query arguments used in the query builder.
- A columns request, used to determine which columns are available without fetching any data.
- A new session request, used to retrieve the actual data from an ad hoc data source
The type of request also determines which life cycle methods are used.
Detailed life cycle overview
The following life cycle methods exist for ad hoc data sources:
| Method | Interface | Required | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| OnInit | IGQIOnInit | No | Always |
| GetInputArguments | IGQIInputArguments | No | Always |
| OnArgumentsProcessed | IGQIInputArguments | No | Always |
| GetColumns | IGQIDataSource | Yes | Always |
| Optimize | IGQIOptimizableDataSource | No | From DataMiner 10.5.0 [CU2]/10.5.5 onwards when using the GQI DxM |
| OnPrepareFetch | IGQIOnPrepareFetch | No | Always |
| OnStartUpdates | IGQIUpdateable | No | From DataMiner 10.4.4/10.5.0 onwards |
| GetNextPage | IGQIDataSource | Yes | Always |
| OnStopUpdates | IGQIUpdateable | No | From DataMiner 10.4.4/10.5.0 onwards |
| OnDestroy | IGQIOnDestroy | No | Always |
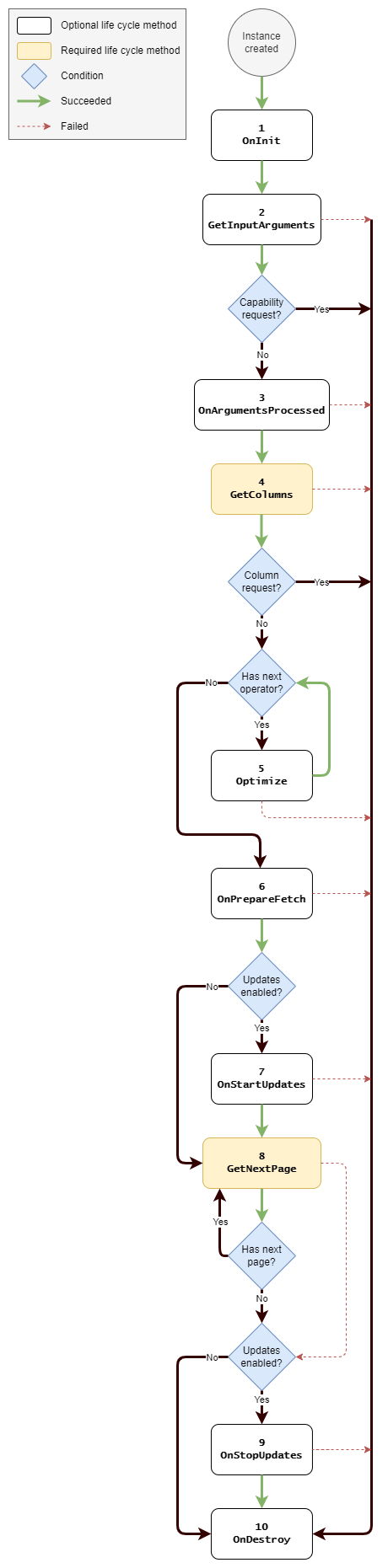
The life cycle methods that are called on an ad hoc data source instance depend on the following conditions:
- The interfaces that are implemented by the associated C# class.
- The type of GQI request for which the instance was created.
- The operators used in the query.
- The query options provided by the client (e.g. whether updates are enabled).
- The result of previous life cycle methods.
The following diagram shows a complete overview of all possible life cycle paths.
OnInit
Building block interface: IGQIOnInit
If implemented, OnInit is always the first life cycle method. It can provide references to dependencies like a logger or an SLNet connection, and it can be used to initialize resources that should be available during the lifetime of the ad hoc data source instance.
Important
Resources that are initialized here should be cleaned up in the final OnDestroy life cycle method.
Note
When resources are only required for specific requests, the initialization should be done in later life cycle methods to avoid unnecessary resource allocations:
- For resources that are only needed to support real-time updates, use the OnStartUpdates life cycle method.
- For resources that are only needed to fetch data, use the OnPrepareFetch life cycle method.
- For resources that are only needed to determine columns, use the GetColumns life cycle method.
GetInputArguments
Building block interface: IGQIInputArguments
If implemented, the GetInputArguments method defines the arguments that can be used to configure the ad hoc data source in a query.
Later, the arguments defined here will determine which argument values are available in the OnArgumentsProcessed life cycle method.
OnArgumentsProcessed
Building block interface: IGQIInputArguments
If implemented, the OnArgumentsProcessed method gives access to the values of the arguments defined in the GetInputArguments life cycle method that were specified in the query.
GetColumns
Building block interface: IGQIDataSource
The GetColumns life cycle method defines the name and type of the columns that are available in the ad hoc data source.
Optimize
Building block interface: IGQIOptimizableDataSource
If implemented, the Optimize life cycle method allows the ad hoc data source to interpret operators that are applied immediately after the data source and potentially adjust its behavior to improve performance of data retrieval.
This life cycle method can be called multiple times for the same instance when the ad hoc data source optimizes the previously applied operator away.
OnPrepareFetch
Building block interface: IGQIOnPrepareFetch
If implemented, the OnPrepareFetch life cycle method allows the ad hoc data source instance to initialize resources that are only needed when fetching data.
If resources are initialized in this method, they should be cleaned up in the final OnDestroy life cycle method.
OnStartUpdates
Building block interface: IGQIUpdateable
If implemented, the OnStartUpdates life cycle method is only called when updates are enabled in the query options. It allows the ad hoc data source instance to initialize any resources that are required to support real-time updates such as subscriptions and event handlers.
Important
Resources that are initialized here should be cleaned up in the OnStopUpdates life cycle method.
GetNextPage
Building block interface: IGQIDataSource
The GetNextPage life cycle method defines the actual data for the ad hoc data source instance. It will be called at least once and can subsequently be called again multiple times as long as the previous GetNextPage call indicates that more pages are available.
OnStopUpdates
Building block interface: IGQIUpdateable
If implemented, the OnStopUpdates life cycle method is only called when updates were enabled in the query options. It allows the ad hoc data source instance to clean up any resources that were initialized in the OnStartUpdates life cycle method to support real-time updates.
Important
The OnStopUpdates life cycle method will not be called when the OnStartUpdates life cycle method failed.
OnDestroy
Building block interface: IGQIOnDestroy
If implemented, OnDestroy is always the last life cycle method. It allows you to clean up any resources that were used during the lifetime of the ad hoc data source instance.
Important
The OnDestroy life cycle method will not be called when the OnInit life cycle method failed.