GQI DxM Architecture
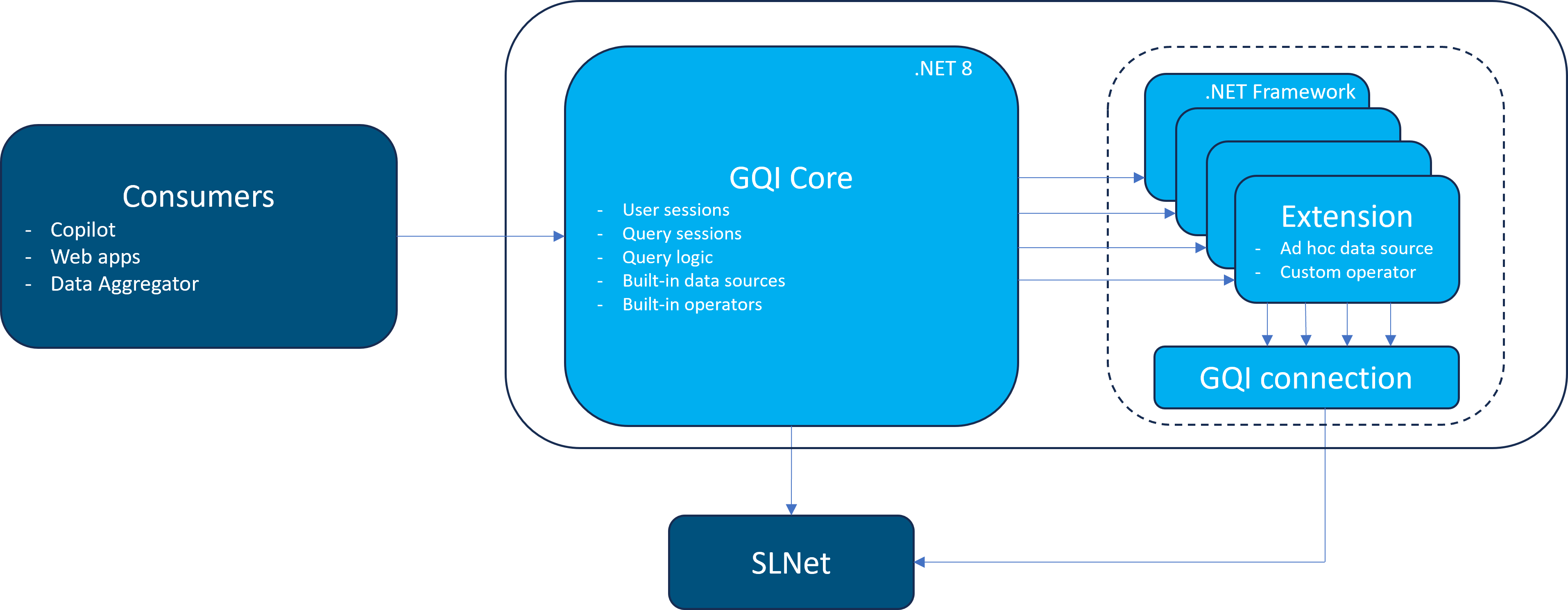
The GQI DxM consists of several processes that work together to handle GQI requests efficiently. Its architecture is designed for modularity, scalability, and effective communication between components.
GQI process overview as of DataMiner 10.5.9
Core process
Process name: DataMiner GQI.exe (Windows Service)
This is the main entry point for all GQI operations. It manages core functionality including query sessions, built-in data sources and operators, and execution of query requests.
When a query uses GQI extensions (like ad hoc data sources or custom operators), the parent process spawns one or more child processes to handle those extensions.
- Technology: .NET 8
- Communication: Connects to the DataMiner Agent via gRPC (APIGateway)
Extension worker processes
Process name: DataMiner GQI.ExtensionsWorker.Automation.exe
Each extension library runs in its own child process, providing isolation and modularity. You can identify which extension a child process is responsible for by checking the command line arguments in Task Manager.
- Technology: .NET Framework 4
The worker process exists as long as it is being used by at least one active query session, and it will remain available if there are no active query sessions until it expires. See Termination of idle child processes.
The worker process can be terminated manually using Task Manager in case an extension is using too many resources or has an issue. In that case, all dependent query sessions will become invalid and will respond with the message "Extension worker for 'ExtensionLibrary' has exited." when you attempt to interact with them.
Communication process
Process name: DataMiner GQI.ExtensionsWorker.SLNet.exe
This process handles communication between GQI extensions and the DataMiner Agent using SLNet. All extensions for a given user share the same SLNet connection to optimize resource use.
- Technology: .NET Framework 4
- Communication: Connects to the DataMiner Agent via IPC (SLNet)