General Feature Release 10.2.4
Note
For known issues with this version, refer to Known issues.
Tip
For information on how to upgrade DataMiner, see Upgrading a DataMiner Agent.
New features
DMS core functionality
New messages that support uploading larger files [ID 32398]
The SLNet process can now use the following new messages to upload files to the DataMiner System.
StartUploadMessage
This message initiates an upload and returns a StartUploadResponse message containing an upload cookie of type int.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DataChunk | byte[] | The initial chunk of data to be uploaded. |
| ReservedSize | long | The total size (in bytes) that should be reserved for the full dataset. |
| Name | string | Optional name of the upload. Naming an upload allows you to retrieve its upload status by means of a FindUploadSlotMessage. |
ContinueUploadMessage
This message continues an already initiated upload and returns an empty ContinueUploadResponse message.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cookie | int | The cookie returned by the StartUploadMessage. |
| DataChunk | byte[] | The next chunk of data to be uploaded. |
| CurrentPosition | long | Optional index location that specifies where the next chunk of data should be appended. Allows you to perform a basic data integrity check. When this location does not match the actual server-side location, the upload will fail. |
Note
- The above-mentioned messages will be used when uploading a large data stream by means of the SendLargeStream method in the SLNetTypes FileUploader helper class.
- The existing SendFile method will use SendLargeStream in the background when it detects a file larger than 2 GB. The default chunk size is 100 KB. When sending large files, it is recommended to slightly increase this default chunk size to prevent a large number of small messages.
- As the AppPackageHelper uses the FileUploader helper class to upload DataMiner packages, it will now also support uploading larger packages.
SNMP forwarding will now take into account alarm storms when resending alarms [ID 32543]
Up to now, when an SNMP Manager was configured to resend all active alarms every configured time interval, it would ignore any ongoing alarm storm. From now on, when there is an alarm storm, depending on whether the Enable alarm storm protection by grouping alarms with the same parameter description option is enabled, the following will happen:
- If the grouping option is enabled, only the alarms that are not associated with an element parameter in alarm storm will be resent.
- If the grouping option is not enabled, no alarms will be resent during the alarm storm.
Note
- When you manually request all alarms to be resent, the logic described above will also apply.
- When inform messages are used instead of traps and the receiving party does not return an acknowledgment, then the retry messages will still be sent, even when an alarm storm starts while those retry messages are being sent.
Service templates: Referencing table parameter cells by means of the primary key [ID 32549]
When configuring a service template, you can use placeholders to reference a parameter value. When referencing a column, up to now, it was only possible to identify a cell by means of the display key. From now on, it is also possible to identify a cell by means of the primary key. See the following example:
[element:1:param:1002:^pk^myPrimaryKey]
New property added to PaToken class: Dictionary<string,DomInstanceId> UserDomInstances [ID 32599]
The PaToken class has a new property: Dictionary<string,DomInstanceId> UserDomInstances.
This is intended to be used in the Process Automation framework.
Process Automation: New ProcessAutomationResourcePool object [ID 32657]
A new Process Automation object class has been created (which inherits the regular ResourcePool class): ProcessAutomationResourcePool
This new object has a property that will be used to store the queue element associated with a resource pool: public ElementId QueueElement
Service & Resource Management: Service templates now also accept ServiceID and ReservationID as input data [ID 32668]
In Service & Resource Management environments, a service template used to generate a service associated with a booking will now also accept a ServiceID and a ReservationID as input data.
DMS Security
SLSSH: Enhanced cypher and key exchange algorithm support [ID 32664]
SLSSH now supports the following additional cyphers and key exchange algorithms:
- AES256CRT
- ECDHSHA2NISTP384
- ECDHSHA2NISTP521
DataMiner now supports the encryption methods detailed below (in order of preference).
HMACs
- HMAC-SHA2-256
- HMAC-SHA1
- HMAC-MD5
Key exchange algorithms
- ecdh-sha2-nistp521
- ecdh-sha2-nistp384
- ecdh-sha2-nistp256
- diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
- diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
- diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1
Ciphers
- Aes-256-CTR
- Aes-128-CTR
- Aes-128-CBC
- 3des-CBC
DMS Protocols
Protocols: Allow for different remote element sources in view table columns [ID 32579]
When setting up remote columns, up to now, all columns had to refer to the same parameter containing a list of remote elements (e.g. “view=:x:y:z”, where x is the ID of the parameter containing the remote element IDs). From now on, it is possible to have two sets of elements referenced by different columns within the same view table.
In the following example, parameters 201 and 301 each contain a list of remote elements, and both can be used within the same view table (in different ColumnOption tags).
<ColumnOption idx="3" pid="2004" type="retrieved" options=";view=:201:1000:3"/>
<ColumnOption idx="4" pid="2005" type="retrieved" options=";view=:301:1000:4"/>
DMS Cube
Visual Overview: Specifying a remote debugging port for Chromium and Edge browser engines [ID 31792]
Embedded Chromium and Edge browser engines allow external tooling to inspect and manipulate their web browser.
When starting DataMiner Cube, from now on, you can pass a remote debugging port for both Chromium and Edge engines by specifying the following command line options:
- ChromeRemoteDebuggingPort=7001
- EdgeRemoteDebuggingPort=7002
Note that the port number must be between 1024 and 65535.
DataMiner Cube - Users/Groups: Permissions needed to edit group membership [ID 32456]
When opening their user card, from now on, users will only be able to edit group membership if they have the following permissions:
- Administrator permission, or
- Limited administrator permission as well as “Edit all groups” or “Edit own groups” permission
Note
Users only need to have the “Edit own groups” permission to be able to configure a group of which they are a member.
Visual Overview: Shapes that cannot be clicked and had their text trimmed will show a tooltip with the full shape text [ID 32463]
Shapes that cannot be clicked and had their text trimmed by means of a “TextTrimming” option in a shape data field of type TextStyle will now automatically show a tooltip with the full, untrimmed shape text.
New setting to enable the cache of the Chromium browser engine [ID 32534]
In the Computer > Advanced section of the Settings app, you can now use the Enable browser cache setting to enable the cache of the Chromium browser engine.
Enabling this cache has the following advantages:
- Certain web applications will load faster.
- SAML authentication can provide a better single sign-on experience.
Caution
This feature involves a potential security risk. If multiple DataMiner users share the same Windows account on a particular computer, they will also share the same browser cache and, as a consequence, the same authentication on third-party websites.
Visual Overview: Linking a shape to an alarm filter with a System Type filter context [ID 32548]
When you link a shape to an alarm filter, you can specify a filter context. Up to now, it was possible to filter on element, service, view or EPM system name. From now on, it is also possible to filter on EPM system type using the following syntax:
FilterContext=SystemType=X
If you specify a filter context like the one above, the shape will be linked to the alarms of which the “System Type” property is set to “X”. This will allow you, for example, to show the alarm statistics of an EPM object or to create a new alarm tab by clicking the shape in question.
Note
It is also possible to specify a filter context in which both system name and system type are combined. To do so, use the following syntax:
FilterContext=SystemName=X;SystemType=Y
If you specify a filter context like the one above, the shape will be linked to the alarms of which the “System Name” is set to “X” and “System Type” is set to “Y”.
DataMiner Cube - Data Display: Row filter will now be shown when opening the alarm template, trend template or information template for a particular parameter table row [ID 32555]
When, in Data Display, you drill down to a specific row of a parameter table, you can open the alarm template, trend template or information template for that specific row. From now on, if a filter was configured for the table row in question, it will also be shown in the UI.
DataMiner Cube - Alarm Console: Clearer summary alarm values in case of an alarm storm [ID 32608]
When the Alarm Console setting Enable alarm storm protection by grouping alarms with the same parameter description is enabled, during an alarm storm, alarms associated with the same parameter will be grouped under a summary alarm.
Up to now, the value of such a summary alarm would state “Parameter (X alarms)” with X being the number of alarm trees rather than the actual number of alarms.
From now on, the value of a summary alarm will instead state “Parameter (X alarm trees - Y alarms)”. This will allow users to see more clearly how many alarms there are left with the same parameter description and how many trees they represent.
Services app: Service definition type [ID 32667]
When configuring a service definition, you now have to specify its type:
- SRM (default type)
- Skyline Process Automation
- Custom Process Automation
In Visual Overview, this type can be visualized by means of a [ServiceDefinition:...] placeholder. See the following example, in which xxx should be replaced by a service definition GUID.
[ServiceDefinition:xxx,Type]
Note
It is not allowed to duplicate service definitions of type “Skyline Process Automation”. Therefore, the Duplicate option will not be available when you right-click a service definition of that type.
Trending: Refresh rate of trend graphs can now be configured [ID 32715]
Up to now, open trend graphs were automatically refreshed every 2 minutes. From now on, you can specify a custom refresh rate (5 seconds to 5 minutes) in the Update interval setting, located in the User > Trending section of the Settings app.
Default: 2 minutes
Note
- Changing this refresh rate can have a minor effect on overall performance, especially when opening trend graphs with more than 10 parameters.
- If you change the Update interval setting, then open trend graphs need to be closed and re-opened if you want them to use the new interval.
Visual Overview: Configuring a shape to set a duration in a session variable [ID 32716]
You can now configure a shape to set a duration of type TimeSpan in a session variable.
To do so, add the following shape data fields to the shape:
- a shape data field of type SetVar, of which the value is set to the name of the session variable, and
- a shape data field of type SetVarOptions, of which the value is set to “Control=Duration”, followed by the necessary options. For a list of possible options, see below.
| Shape data field | Value |
|---|---|
| SetVar | <name of session variable> |
| SetVarOptions | Control=Duration|<option>|<option>|... |
Options
Next to “Control=Duration”, you can specify the following options (separated by pipe characters).
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| ShowInfinity=true/false | When this option is set to true, next to the duration selector, a checkbox is displayed that can be used to set the duration to infinity, which will replace the value of the session variable with TimeSpan.MaxValue. Default: False. |
| Minimum= | The minimum duration. Default: 1 minute. |
| Maximum= | The maximum duration. Default: 1 week. |
Setting the initial value of the duration in the session variable
Use a page-level InitVar field to set the initial value of the duration in the session variable.
If you set the initial value to “Infinity”, the value in the session variable will be replaced by TimeSpan.MaxValue. If the ShowInfinity option is set to true, a selected infinity checkbox will be displayed next to the duration selector.
Note
Using an InitVar or SetVar field, it is possible to set a duration that is outside of the specified minimum/maximum range.
Specifying a duration
When specifying the minimum duration, the maximum duration and the InitVar value, you can use the following units:
| Unit | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| No unit | If no unit is specified, then the number in question will be considered a number of days. | 1 |
| s | seconds | 1s |
| m | minutes | 1m |
| h | hours | 1h |
| d | days | 1d |
| mo | months (1 month = 30 days) | 1mo |
| y | years (1 year = 365 days) | 1y |
DMS Reports & Dashboards
Dashboards app - Node edge graph: Option to visualize the direction of the edges [ID 32519]
When configuring a node edge graph, it is now possible to have the graph visualize the direction of the edges.
To do so, enable the Visualize directions setting and select one of the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Flow (default) | The direction is visualized by means of animated edges. |
| Arrows | The direction is visualized by means of arrows drawn on the edges. If you select this option, you can also specify the exact position of the arrows on the edges. |
Dashboards app - Parameter feed: 'Selected only' toggle button has been removed [ID 32541]
Up to now, a parameter feed had a Selected only toggle button that allowed you to show or hide items that were not selected. Now, this toggle button has been removed.
Also, when a dashboard is loaded with an initial selection (either configured or in the URL), the selected items will now always appear at the top of the list.
Dashboards app - GQI: GQI filter can now be linked to query rows [ID 32552]
In a filter node of a dashboard query, you can now choose to filter by query rows from a feed. To do so, select the Use feeds option, select the feed, select the type Query rows, and then select the appropriate column of the table containing the rows. Note that only the columns compatible with the type of column you are filtering will be available for selection.
Dashboards app: Specifying data input for an EPM feed in a URL using 'epm-selections' instead of 'cpes' [ID 32594]
Up to now, in a dashboard URL, it was possible to specify data input for an EPM feed by means of a “cpes” data key. This key has now been deprecated in favor of the new “epm-selections” key.
The new “epm-selections” data key consist of the following elements:
- DataMiner ID
- Element ID
- Field parameter ID
- Primary key
The following example shows a JSON object that contains an “epm-selections” data key, which can be passed to a dashboard using a URL parameter of type “data”:
{
"version": 1,
"feed": {
"epm-selections": ["111/222/333/index"]
}
}
Note
In order to maintain backward compatibility, data provided via a “cpes” object will automatically be converted when necessary. Only when any of the fields in the “cpes” object contain forward slashes will you need to use the new “epm-selections” object instead.
Dashboards app: Default index filter for parameter feed component [ID 32595]
It is now possible to add a default index filter to a parameter feed component. This way, it's not necessary to apply your filter to the component again whenever the dashboard is refreshed.
This new option is available as an advanced setting that is not displayed by default. To be able to configure it, you therefore first need to add the showAdvancedSettings=true option to the dashboard URL. In the Data pane of the dashboard edit mode, a new Parameter table filters section will then become available. You can configure the default filter in this section and then drag it to a component to apply it.
Dashboards app: 'Write' filter removed from Data > All available data > Parameters [ID 32643]
When, after selecting a component in edit mode, you open the Data tab and go to the All available data > Parameters section, you can select an element and then filter the list of parameters of that element by clicking a number of preset filters. The preset filter “Write”, which was used to filter out the parameters of type “write”, has now been removed.
Dashboards app: GQI now supports external data [ID 32656][ID 32659][ID 32930]
It is now possible to configure the Generic Query Interface to retrieve external data, so that dashboard users can use a query data source based on data that is for example retrieved from a CSV file, a MySQL database, or an API endpoint. This is configured through a DataMiner Automation script that is compiled as a library. The GQI will make use of this library to load the external data.
Configuring an external data source in a query
This is the most basic procedure to use an external data source in a query:
In the Automation app, add a script containing a new class that implements the IGQIDatasource interface (see below for more detailed info).
Above the class, add the GQIMetaData attribute in order to configure the name of the data source as displayed in the Dashboards app.
For example (see Example script for a full example):
using Skyline.DataMiner.Analytics.GenericInterface; [GQIMetaData(Name = "People")] public class MyDataSource : IGQIDataSource { ... }Note
This is the name that will be shown to the user when they select the data in the Dashboards app. If you do not configure this name, the name of the class is displayed instead, which may not be very user-friendly.
Compile the script as a library. You can use the same name as defined in the GQIMetaData attribute, or a different name. If there are different data sources for which the same name is defined in the GQIMetaData attribute, the library name is appended to the metadata name.
Validate and save the script. It is important that you do this after you have compiled the script as a library, as otherwise the compiler will detect errors.
In the Dashboards app, configure a query and select the data source Get custom data.
In the Data source dropdown box, select the name of your custom data source.
Depending on how the script is configured, there can be additional configuration possibilities. You can for instance use the IGQIInputArguments interface in the script to define that a specific argument is required, for instance to filter the displayed data. For more information, refer to the sections below.
Interfaces
A custom data source is represented as a class that implements predefined interfaces. The interfaces you can use are detailed below.
IGQIDataSource: This is the only required interface. It must be implemented for the class to be detected by GQI as a data source. This interface has the following methods:
Method Input arguments Output arguments Description GetColumns GQIColumn[] The GQI will request the columns. GetNextPage GetNextPageInputArgs GQIPage The GQI will request data. IGQIInputArguments: This interface can be used to have the user specify an argument, for example the CSV file from which data should be parsed, or a filter that should be applied. This interface has the following methods:
Method Input arguments Output arguments Description GetInputArguments - GQIArgument[] Asks for additional information from the user when the data source is configured. OnArgumentsProcessed OnArgumentsProcessedInputArgs OnArgumentsProcessedOutputArgs Event to indicate that the arguments have been processed. Note
The GQI does not validate the input arguments specified by the user. For example, a user can input an SQL query as a string input argument, and the content of the string argument will be forwarded to the custom data source implementation without validation.
IGQIOnInit: This interface is called when the data source is initialized, for example when the data source is selected in the query builder or when a dashboard using a query with custom data is opened. It can for instance be used to connect to a database. This interface has one method:
Method Input arguments Output arguments Description OnInit OnInitInputArgs OnInitOutputArgs Indicates that an instance of the class has been created. IGQIOnPrepareFetch: This interface is used to implement optimizations when data is retrieved. This can for instance be used to limit the retrieved data. This interface has one method:
Method Input arguments Output arguments Description OnPrepareFetch OnPrepareFetchInputArgs OnPrepareFetchOutputArgs Indicated that the GQI has processed the query. IGQIOnDestroy: This interface is called when the instance object is destroyed, which happens when the session is closed, e.g. in case of inactivity or when all the necessary data has been retrieved. It can for instance be used to end the connection with a database. This interface has one method:
Method Input arguments Output arguments Description OnDestroy OnDestroyInputArgs OnDestroyOutputArgs Indicates that the GQI will close the session.
Lifecycle
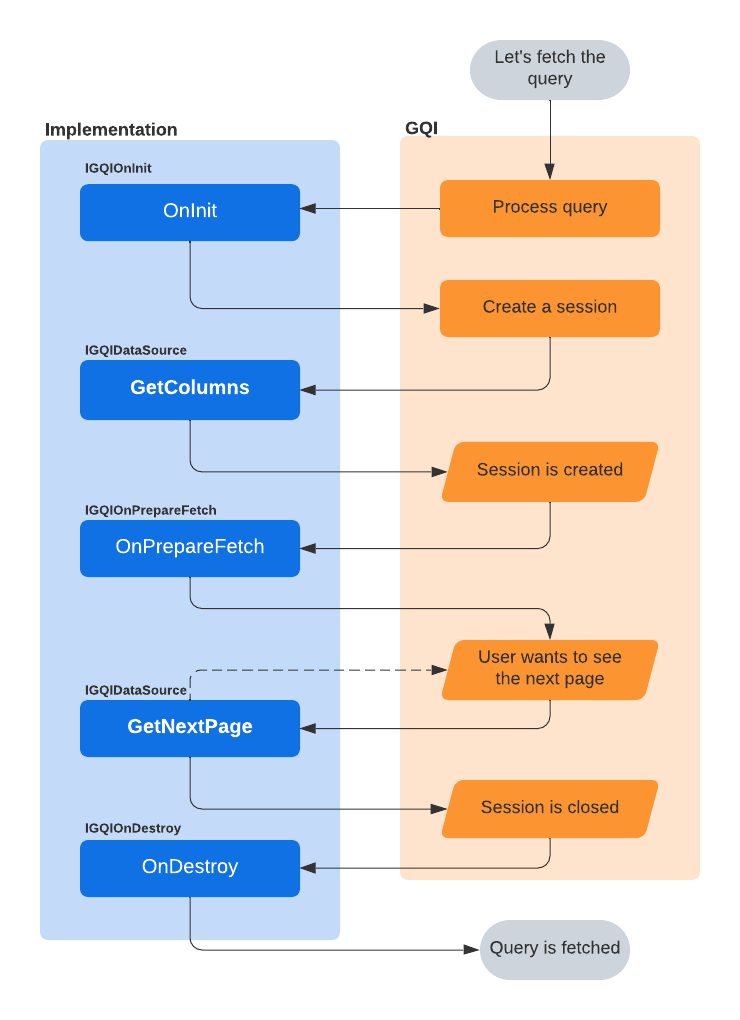
All methods discussed above are called at some point during the GQI lifecycle, depending on whether a query is created or fetched, and depending on whether they have been implemented.
The following flowchart illustrates the GQI lifecycle when a query is created:
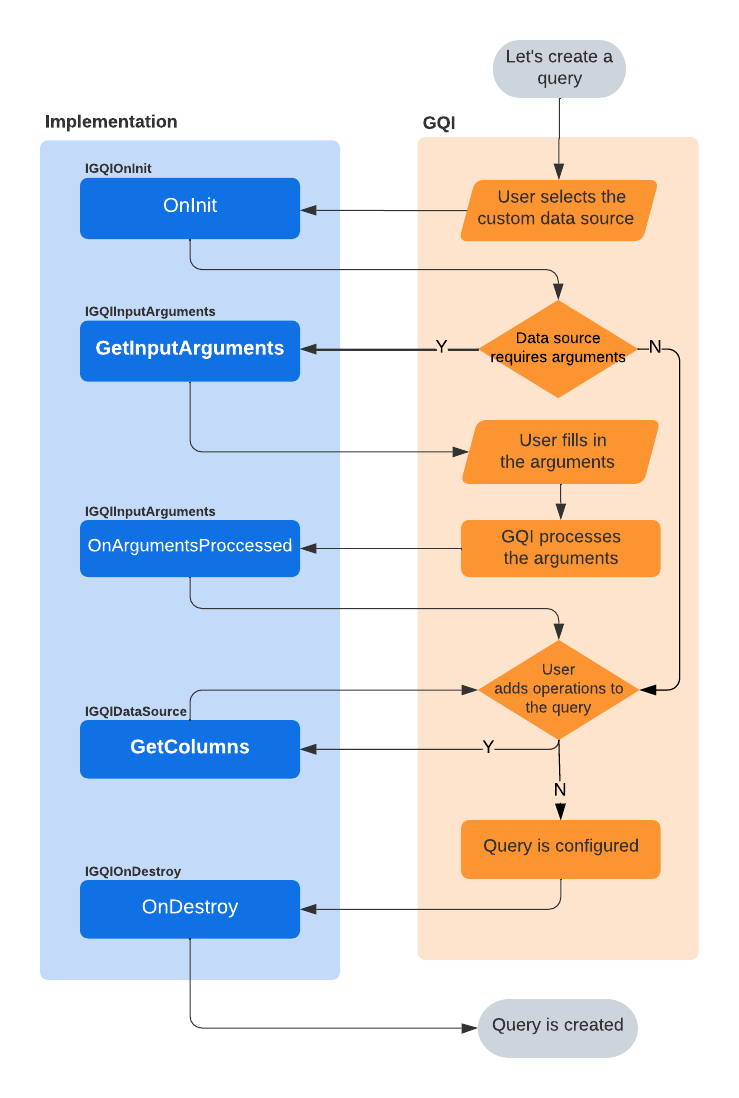
The following flowchart illustrates the GQI lifecycle when a query is fetched:
Objects
To build the custom data source, you can use the objects detailed below.
GQIColumn: This is an abstract class with the derived types GQIStringColumn, GQIBooleanColumn, GQIIntColumn, GQIDateTimeColumn and GQIDoubleColumn and with the following properties::
Property Type Required Description Name String Yes The column name. Type GQIColumnType Yes The type of data in the column. GQIColumnType is an enum that contains the following values: String, Int, DateTime, Boolean or Double. GQIPage, with the following properties:
Property Type Required Description Rows GQIRow[] Yes The rows of the page. HasNextPage Boolean No True if additional pages can be retrieved, False if the current page is the last page. GQIRow, with the following properties:
Property Type Required Description Cells GQICell[] Yes The cells of the row. GQICell, with the following properties:
Property Type Required Description Value Object No The value of the cell. DisplayValue String No The display value of the cell. Note
The type of value of a cell must match the type of the corresponding column.
GQIArgument: This is an abstract class, with the derived types GQIStringArgument and GQIDoubleArgument, and with the following properties:
Property Type Required Description Name String Yes The name of the input argument. IsRequired Boolean No Indicates whether the argument is required.
Example script
Below you can find an example script that forwards dummy data to the GQI. The name of the data source, as defined in the GQIMetaData attribute, will be “People”.
First the IGQIDataSource interface is implemented, then GetColumns is used to define the custom columns for the data source. In this case, there are 5 columns. The GetNextPage method then returns the actual data to the GQI. In this case these are 3 rows, defined as an array of cells. For each cell, a display value can also be defined. In this case, this is done for the cells within the Height column to indicate the unit of measure. The HasNextPage property is set to False to indicate that no additional pages need to be fetched.
The optional IGQIInputArguments interface is also implemented in the example, in this case to allow the user to add an input argument indicating the minimum age for the records that will be retrieved. The argument is indicated as required, so the user will have to specify it to be able to configure the query. The argument value is retrieved with OnArgumentsProcessedInputArgs and used to filter the returned data.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using Skyline.DataMiner.Analytics.GenericInterface;
[GQIMetaData(Name = "People")]
public class MyDataSource : IGQIDataSource, IGQIInputArguments
{
private GQIDoubleArgument _argument = new GQIDoubleArgument("Age") { IsRequired = true };
private double _minimumAge;
public GQIColumn[] GetColumns()
{
return new GQIColumn[]
{
new GQIStringColumn("Name"),
new GQIIntColumn("Age"),
new GQIDoubleColumn("Height (m)"),
new GQIDateTimeColumn("Birthday"),
new GQIBooleanColumn("Likes apples")
};
}
public GQIArgument[] GetInputArguments()
{
return new GQIArgument[] { _argument };
}
public OnArgumentsProcessedOutputArgs OnArgumentsProcessed(OnArgumentsProcessedInputArgs args)
{
_minimumAge = args.GetArgumentValue(_argument);
return new OnArgumentsProcessedOutputArgs();
}
public GQIPage GetNextPage(GetNextPageInputArgs args)
{
var rows = new List<GQIRow>() {
new GQIRow(
new GQICell[]
{
new GQICell() { Value = "Alice" },
new GQICell() { Value = 32 },
new GQICell() { Value = 1.74, DisplayValue = "1.74 m" },
new GQICell() { Value = new DateTime(1990, 5, 12) },
new GQICell() { Value = true }
}),
new GQIRow(
new GQICell[]
{
new GQICell() { Value = "Bob" },
new GQICell() { Value = 22 },
new GQICell() { Value = 1.85, DisplayValue = "1.85 m" },
new GQICell() { Value = new DateTime(2000, 1, 22) },
new GQICell() { Value = true }
}),
new GQIRow(
new GQICell[]
{
new GQICell() { Value = "Carol" },
new GQICell() { Value = 27 },
new GQICell() { Value = 1.67, DisplayValue = "1.67 m" },
new GQICell() { Value = new DateTime(1995, 10, 3) },
new GQICell() { Value = false }
})
};
var filteredRows = rows.Where(row => (int)row.Cells[1].Value > _minimumAge).ToArray();
return new GQIPage(filteredRows)
{
HasNextPage = false
};
}
}
Dashboards app: User groups can now be selected in dashboard security [ID 32681]
When you configure who can view or edit a specific dashboard, it is now possible to select entire user groups instead of only individual users. Groups are indicated with a different icon to make the difference clear. In the selection box, they are listed together with individual users. Natural sorting is applied, with individual users being sorted by full name and groups being sorted by group name.
DMS web apps
Jobs app: Delete button will only be visible to users who have been granted permission to delete jobs [ID 32507]
From now on, the Delete button will only be visible to users who have been granted permission to delete jobs.
DMS Service & Resource Management
Service & Resource Management: Updated exceptions thrown when the time range of a child ReservationInstance or child ReservationDefinition is invalid [ID 32581]
The following exception messages have been enhanced.
Exception thrown when the time range of a child ReservationInstance is invalid
This message now includes the ID, the name and the time range of both the parent and the child.
The TimeRange of the child is not within the boundaries of the parent ReservationInstance (Child: '{Child Name}' ({Child ID}) has range '{Child Range}' & Parent: '{Parent Name}' ({Parent ID}) has range '{Parent Range}')
Exception thrown when the time range of a child ReservationDefinition is invalid
This message now includes the ID, the name and the time range of both the parent and the child. For the child, the offset has now also been added.
The timing of the child is not within the boundaries of the parent ReservationDefinition (Child: '{Child Name}' ({Child ID}) has timing with duration '{Child Timing Duration}' and offset '{Child offset}' & Parent: '{Parent Name}' ({Parent ID}) has timing with duration '{Parent Timing Duration}')
ReservationInstances now have a ReservationInstanceType [ID 32624]
When configuring a ReservationInstance, you now have to specify a ReservationInstanceType:
- Default
- Process Automation
- Custom Process Automation
Note
- In case of a ServiceReservationInstance, the type of the instance must be identical to the type of the ServiceDefinition. Otherwise, the ResourceManager will throw a “ServiceDefinitionTypeDoesNotMatch” error.
- A new exposer has been added to allow filter ReservationInstanceType.
Modified AbsoluteQuarantinePriority behavior and several new SRM features [ID 32654]
Several changes to the SRM framework have been introduced:
- Modified AbsoluteQuarantinePriority behavior.
- New ConcurrencyUsageType property for ResourceUsageDefinition
- Possibility to book complete resource capacity
- Possibility to include elements in bookings
Modified AbsoluteQuarantinePriority behavior
The behavior of the AbsoluteQuarantinePriority property has been modified. Up to now, if this property was set to true for a booking instance, all overlapping booking instances using the same resources were forced into quarantine. Now this property will only determine the priority of the booking when a quarantine is needed.
To implement a quarantine, overbooked capacity is now removed from bookings according to the following order of priority:
- Bookings that are already in the quarantined state.
- Bookings for which AbsoluteQuarantinePriority is not specified or false.
- Bookings that are in a "Pending" state.
- Bookings with the latest start time.
- Booking of which the name comes last alphabetically.
- Bookings of which the GUID comes last alphabetically.
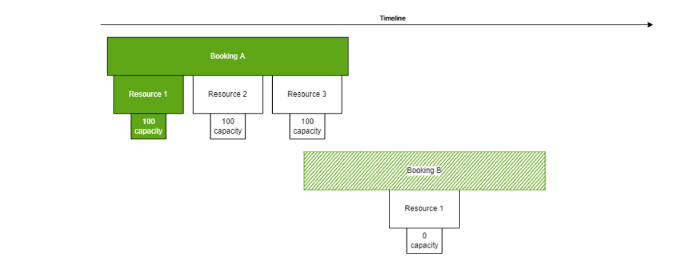
The image below illustrates a situation where the quarantine behavior has changed. Previously, booking A would have been quarantined, as it uses resource 1. Now this will no longer happen as the capacity is actually not overbooked.
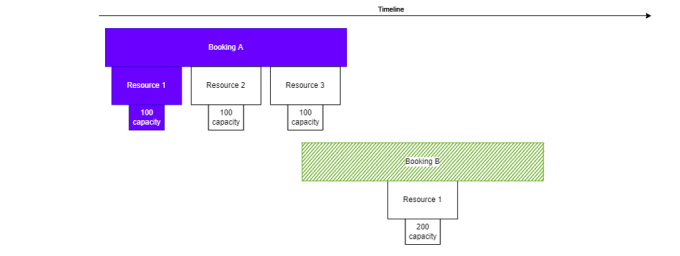
The following image also illustrates the modified behavior. If booking B does not have AbsoluteQuarantinePriority set to true, its capacity will be moved, as it has a later start time. If AbsoluteQuarantinePriority is set to true, the overbooking will be resolved by moving the capacity from booking A.
New ConcurrencyUsageType property for ResourceUsageDefinition
A ResourceUsageDefinition now has the property ConcurrencyUsageType, which can have the following values:
- ConcurrencyUsageType.Default: The default value. The ResourceUsageDefinition takes one concurrency of the resource.
- ConcurrencyUsageType.All: The ResourceUsageDefinition takes all the concurrency of the resource.
- ConcurrencyUsageType.None: The ResourceUsageDefinition does not take any concurrency of the resource.
Resource usage can only overlap with a ResourceUsageDefinition with ConcurrencyUsageType.All if it is set to ConcurrencyUsageType.None. This limitation is also in place for a single booking: if a booking has a resource with complete concurrency and another resource with 1 concurrency, the booking will be quarantined because it requests more concurrency than is available. If a complete concurrency usage is quarantined to resolve a concurrency conflict (as determined by the priority defined on booking level), it will be moved in its entirety – there is no option to only move part of the concurrency to quarantine.
The actual concurrency of a ResourceUsageDefinition with ConcurrencyUsageType.All is determined at runtime, as the MaxConcurrency value of the resource at the moment when it is needed, e.g. when GetEligibleResources is called or when quarantine checks are done to add or update a booking instance or resource.
Code example:
var booking = new ReservationInstance(new TimeRangeUtc(DateTime.UtcNow, DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(10)))
{
Name = "Booking 123",
ID = Guid.NewGuid()
};
var resourceUsage = new ResourceUsageDefinition(resourceId)
{
ConcurrencyUsageType = ConcurrencyUsageType.All
};
booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance.Add(resourceUsage);
Booking complete resource capacity
It is now possible to book all the capacities of a resource for their complete value, by setting the UsesCompleteCapacity property for the ResourceUsageDefinition to true. If the resource has more than one capacity defined, this will reserve all capacities. By default, this property is set to false.
No other usage can overlap in case complete capacity is used. This limitation is also in place for a single booking: if a booking has a resource with complete capacity and another resource with 100 capacity, the booking will be quarantined because it requests more capacity than is available. If a complete capacity usage is quarantined to resolve a conflict (as determined by the priority defined on booking level), it will be moved in its entirety.
The actual capacity in case UsesCompleteCapacity is true is determined at runtime, e.g. when GetEligibleResources is called or when quarantine checks are done to add or update a booking instance or resource.
Code example:
var booking = new ReservationInstance(new TimeRangeUtc(DateTime.UtcNow, DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(10)))
{
Name = "Booking 123",
ID = Guid.NewGuid()
};
var resourceUsage = new ResourceUsageDefinition(_resource.ID)
{
UsesCompleteCapacity = true
};
booking.ResourcesInReservationInstance.Add(resourceUsage);
Including elements in bookings
It is now possible to define an ElementUsageDefinition to include an element in a booking. When the element is included, ResourceUsageDefinitions will automatically be added for all the resources linked to the element. These resources will have the new IsAutoGenerated property set to true.
ElementUsageDefinition has three properties:
- ElementUsageImpact: Determines if the element can be used in overlapping bookings. If set to None, overlapping bookings can use the same element. If set to Full (the default value), no overlapping bookings can use the same element, even if they have impact None. If the AddOrUpdateReservationInstances call fails because there are overlapping bookings using the same element with Full impact, no changes will be saved and an error of type ElementUsageOverflow will be returned.
- IncludeCapacityBehavior: Can be set to All or None. If this is set to All, the generated ResourceUsageDefinitions will have the UsesCompleteCapacity property set to true.
- IncludeConcurrencyBehavior: Can be set to All or None. If this is set to All, the generated ResourceUsageDefinitions will have the ConcurrencyUsageType property set to ConcurrencyUsageType.All.
Code example:
var booking = new ReservationInstance(new TimeRangeUtc(DateTime.UtcNow, DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(10)))
{
Name = "Booking 123",
ID = Guid.NewGuid()
};
var elementUsage = new ElementUsageDefinition(new ElementID(123,456))
{
ElementUsageImpact = ElementUsageImpact.Full,
IncludeCapacityBehavior = IncludeCapacityBehavior.All,
IncludeConcurrencyBehavior = IncludeConcurrencyBehavior.All
};
booking.ObjectUsages.Add(elementUsage);
The following resources are added when an element is included in a booking:
- Resources that reference the element with the DmaID and ElementID properties.
- Function resources that have the referenced element as their parent element (based on MainDveDmaId and MainDveElementId properties).
- Virtual function resources linked to the element (based on PhysicalDeviceDmaId and PhysicalDeviceElementId properties).
Whenever the booking is updated or a relevant resource is created or updated, the element usage is automatically updated. Any changes you do to auto-generated usage will be overwritten by the core software. When the auto-generated usage is updated, the TraceData of the AddOrUpdateResource call will contain ResourceManagerInfoData of type ResourceUsagesGeneratedForReservationInstances.
The deletion of resources in auto-generated bookings is blocked in the same way as deletion of resources that were not added automatically is blocked.
This new feature has an ElementUsages exposer, which can be used to filter bookings that include a certain element. For example:
var elementToSearchFor = new ElementID(123, 789);
var filter = ReservationInstanceExposers.ElementUsages.Contains(elementToSearchFor.ToString());
var bookings = rmHelper.GetReservationInstances(filter);
Changes
Enhancements
Security enhancements [ID 32566]
A number of security enhancements have been made.
DataMiner is now able to connect to Cassandra databases that require TLS 1.2 [ID 31852]
DataMiner is now able to connect to Cassandra databases that require TLS 1.2.
Cassandra will no longer store ArrowWindowRecords and PatternMatchOccurrenceRecords [ID 31944]
Cassandra databases will no longer store the following data:
- ArrowWindowRecords
- PatternMatchOccurrenceRecords
The latter will now be stored in Elasticsearch instead.
SLElement: Enhanced performance when resolving table relationships [ID 32176]
Due to a number of enhancements, overall performance of SLElement has increased when resolving table relationships.
Filtered subscriptions will now be processed similarly to non-filtered subscriptions [ID 32399]
Filtered subscriptions will now be processed similarly to non-filtered subscription, regardless of whether the element in question is hosted on the local DMA or a remote DMA.
DataMiner backups will now by default also include SSL certificates and EPMConfig.xml files [ID 32504]
Full backups and configuration backups will now by default also include the EPMConfig.xml files and all certificates used by protocols for encrypted communication with devices.
DataMiner Cube - Correlation: Using hidden elements when creating correlation rules [ID 32510]
When creating a correlation rule in the Correlation app, it is now possible to use a hidden element in both the Alarm Filter section and the Rule Condition section.
Enhanced performance when stopping SNMP elements [ID 32523]
Due to a number of enhancements, overall performance has increased when stopping SNMP elements.
DataMiner Cube - Automation: SaveAutomationScriptXmlMessage will now be used when importing, saving and updating Automation scripts [ID 32557]
Up to now, when an Automation script was imported, the file would not be processed in the same way as when an Automation script was saved or updated. From now on, the same SaveAutomationScriptXmlMessage will be used when importing, saving and updating Automation scripts.
Hanging threads in SLNet will now be logged in SLHangingCalls.txt [ID 32582]
Up to now, hanging threads in SLNet would be logged in the SLNet.txt file. From now on, these will be logged in the new SLHangingCalls.txt file instead (without the stack trace).
This file will by default be refreshed every 5 minutes.
DataMiner Cube - Spectrum analysis: Additional logging to help pinpoint monitor failures [ID 32605]
When, on a spectrum element card, you select View buffer in the monitors tab of the ribbon, the selection boxes should contain all available monitor buffers.
In DataMiner Cube, additional logging is now available to help pinpoint monitor execution failures by providing information about the monitor buffers that will be shown based on the backend buffer response.
DataMiner Cube: Information templates will only show the read parameter in case of a toggle button [ID 32610]
Up to now, for a write parameter configured as a toggle button, an information template would show two parameters: a read parameter and a write parameter. From now on, toggle buttons will be treated as regular parameters. In an information template, only the read parameter (of type discreet) will be shown.
Video thumbnails: New options for HTML5 video player & VLC player [ID 32626]
The HTML5 video player and the VLC player have a number of new options.
HTML5 video player
The HTML5 video player will now by default mute videos when played automatically.
VLC player
When playing videos using the VLC player, it is now possible to specify the volume in the URL. See the following example. The volume has to be specified as a percentage (0 to 100). Default: 0 (i.e. muted).
https://dma.local/VideoThumbnails/Video.htm?type=VLC&source=https://videoserver/video.mp4&volume=50
HTML5 video player & VLC player
Using the HTML video player or the VLC player, it is now possible to specify whether a video should be played in a loop. See the following example. Default: false
https://dma.local/VideoThumbnails/Video.htm?type=HTML5&source=https://videoserver/video.mp4&loop=true
Enhanced performance of the interprocess communication between SLDataGateway and SLAnalytics [ID 32653] [ID 32709]
Due to a number of enhancements, overall performance of the interprocess communication between SLDataGateway and SLAnalytics has increased.
Server processes will now use InvariantCulture [ID 32665] [ID 32912]
Up to now, server processes like SLNet used the default system locale. If this locale was a language other than English, all internal .NET Framework exception stack traces and log messages would be generated in that language, making it harder to interpret or analyze them. From now on, the server processes will now force their threads to use the CultureInvariant culture by default.
Note
SLManagedAutomation and SLManagedScripting will continue to use the default system locale.
Backups will now by default also include the SLAnalytics configuration [ID 32699]
Full backups and configuration backups will now by default also include the SLAnalytics configuration.
DataMiner Cube - Automation: Specifying an offset value will now be optional in case of a Set action [ID 32743]
When, in an Automation script, you configured a Set action for which an offset value could be specified, up to now, it was mandatory to specify that offset value. From now on, specifying an offset value will be optional. Either select “with value offset” and enter a value, or select “without value offset”.
Default: “without value offset”
Size of SLMessageBroker.txt log file is now limited to 3MB [ID 32863]
The size of the SLMessageBroker.txt log file is now limited to 3MB.
NATS: Enhanced handling of serialization issues [ID 32883]
A number of enhancements have been made with regard to the handling of serialization issues.
Fixes
Failover: Cassandra nodes would not be removed from the Cassandra cluster when a Failover configuration was ended [ID 29894]
When a Failover configuration was ended, in some cases, the Cassandra nodes would not be removed from the Cassandra cluster. From now on, the Cassandra nodes on the main and the backup agent will each be properly removed from the Cassandra cluster and become single nodes.
Note
After ending a Failover configuration, it is recommended to check the nodetool status on both nodes to make sure the nodes no longer form a cluster.
Cassandra: Problem when reading DVEElementInfo rows that contained NULL values [ID 32357]
Up to now, DataMiner could throw an exception when reading a DVEElementInfo row that contained NULL values.
SNMP forwarding: Problem when deleting an SNMP manager and immediately creating an identical one [ID 32406]
When you deleted an SNMP manager of type SNMPv3 and then immediately created an identical one, in some rare cases, an exception of type “Float Invalid Operation” would be thrown.
Dashboards: No longer possible to switch between visualizations when a component did not require data [ID 32413]
When you hovered over a component that did not require data (e.g. text, clock, image, etc.), it would no longer be possible to select another visualization.
DataMiner Cube - Services app: Expand/collapse button in front of a service profile definition would disappear when you expanded or collapsed the service profile definition node [ID 32439]
When, in the Profiles tab of the Services app, you expanded or collapsed a service profile definition node in the tree on the left, the expand/collapse button in front of that service profile definition would incorrectly disappear. In other words, there was no way to reverse the expand/collapse action.
DataMiner Cube - Data Display: Not possible to open the alarm template or trend template of a parameter that was not trended [ID 32449]
When, in Data Display, you drill down to a parameter of an element, you can configure the alarm and trend templates for that specific parameter. When you tried to configure the alarm template or the trend template of a parameter that can be trended but wasn’t, up to now, it would incorrectly not be possible to open the alarm template or trend template of that specific parameter.
DataMiner Cube - Profiles app: Problem when trying to retrieve mediation snippets and service profiles on a system without ElasticSearch database [ID 32488] [ID 32539]
When you tried to open the Profiles app on a DataMiner System with a Service Manager license that did not have an ElasticSearch database, the app would fail to initialize when attempting to retrieve mediation snippets and service profiles. From now on, the presence of an ElasticSearch database will be checked before trying to retrieve mediation snippets and service profiles.
Note
On systems without an ElasticSearch database, it is not possible to configure mediation snippets.
Stopping an SNMPv3 element could have a negative impact on the overall performance of other SNMPv3 elements [ID 32498]
Up to now, in some cases, stopping an SNMPv3 element could have a negative impact on the overall performance of other SNMPv3 elements.
Problem when trying to delete a protocol [ID 32522]
In some cases, an error could occur when you tried to delete a protocol.
Dashboards app: Not possible to share a dashboard immediately after connecting a DMA to the cloud [ID 32547]
When you tried to share a dashboard immediately after the DataMiner Agent had been connected to the cloud, in some cases, an error would appear, saying that the DataMiner Agent was not connected to the cloud.
Dashboards: Problem when sharing a dashboard created in an earlier version of the Dashboards app [ID 32551]
If you tried to share a dashboard that was created in an earlier version of the Dashboards app, in some cases, an error could occur.
Web services API: Problem with internal GQI calls when web sockets were disabled [ID 32570]
When web sockets were disabled on the DataMiner Agent, in some cases, internal GQI calls could throw exceptions.
SLProtocol would leak memory when using a 'change after response' trigger [ID 32572]
When using a “change after response” trigger, SLProtocol would leak memory on every incoming response. See the following example.
<Trigger id="2">
<On id="1">parameter</On>
<Time>change after response</Time>
<Type>action</Type>
<Content>
<Id>2</Id>
</Content>
</Trigger>
Elasticsearch: Problem when using a filter that checked whether a string was empty [ID 32586]
In some cases, Elasticsearch would return an incorrect number of records when a query contained a filter that checked whether a string was empty in combination with other filters.
Elasticsearch: Page would return empty when requesting the next page of naturally sorted data [ID 32596]
When the next page of naturally sorted data was requested from an Elasticsearch database, up to now, that page would return empty.
Jobs app: No 'loading' indication when job sections were being loaded [ID 32616]
When configuring jobs, no “loading” indication would appear when job sections were being loaded.
Dashboards app: Shared dashboards still showed 'Share' option [ID 32618]
When you clicked the “...” button in the top-right corner of a shared dashboard, the menu would incorrectly include a “Share” command.
As it is not possible to share a dashboard that has already been shared, this command will no longer be available when you open a shared dashboard.
DataMiner Cube: Pop-up window asking for new password disappeared after a while [ID 32623]
When an administrator enables the “User must change password at next login” setting for a particular local DataMiner user, the next time that user tries to log in to DataMiner Cube, a pop-up window will appear, asking to enter a new password. In some cases, that pop-up window could disappear after a while, even though no new password had been specified.
Web services API: Problem with GetServiceTemplate [ID 32625]
The GetServiceTemplate method would throw an exception when requesting a service template with Text inputs that had neither of the following options:
- Require a valid element name
- Allow 'N/A' to indicate empty value
SLNet would leak memory whenever a Cube session was closed or disconnected [ID 32649]
Whenever a Cube session was closed or disconnected, SLNet would leak memory.
Miscellaneous small fixes [ID 32655]
A number of miscellaneous, small fixes have been made.
Dashboards app - Parameter feed: Problem selecting the element again after clicking 'Clear all' [ID 32661]
When, in a parameter feed with a single element, you clicked the Clear all option to unselect all selected parameter, in some cases, it would no longer be possible to select the element again.
Migration to Cassandra cluster: Alarms and information events would not get migrated [ID 32666]
When migrating single Cassandra nodes to a Cassandra cluster, in some cases, the alarms and information events would incorrectly not get migrated, especially on systems with a large number of alarms and information events.
Serial protocols: Length check would incorrectly take into account the data before the header [ID 32669]
Up to now, when a payload with data before the header was received (e.g. aaaa<header>payloadwithfixedlength), the data before the header would correctly be stripped off before forwarding the payload to the protocol, but the length check would incorrectly take that data into account.
Problem when migrating a Failover system to a Cassandra cluster [ID 32672]
When the Cassandra Cluster Migrator tool was used to transform a Failover system consisting of DMAs with separate SQL or Cassandra databases into a Failover system consisting of DMAs that are all connected to a shared Cassandra and Elasticsearch cluster, in some cases, the migration process would incorrectly be initiated on the offline DMA instead of the online DMA. When that happened, the data written during the migration process would not be written to the destination Cassandra Cluster database.
SLNetClientTest: Problems with 'Agent Connections' window [ID 32679]
When, in the SLNetClientTest tool, you opened the Agent Connections window (by selecting Diagnostics > Connections > View DMA Connections),
- Agents could incorrectly display a “Disconnected” state while actually being connected.
- The “Calls From” column could incorrectly display “(not available)”.
DataMiner Cube - Profiles app: Problem when modifying a profile instance [ID 32688]
When a profile instance is modified, the existing instance is copied and the modifications are done on the properties of the newly created copy. However, up to now, the parameter entries of the profile instance would incorrectly not get copied. Instead, new parameter entries would be created. From now on, the parameter entries of the profile instance will be copied along.
DataMiner Cube - Alarm templates: Table conditions would no longer be saved correctly [ID 32691]
When, in an alarm template, you specified table conditions, in some cases, those conditions would no longer be saved correctly.
Dashboards: Missing sidebar when navigating to a dashboard URL for edit mode without having edit access [ID 32706]
When you navigate to a dashboard via a URL containing the edit=true parameter, and you do not have permission to edit that dashboard, the dashboard will not be opened in edit mode.
However, up to now, when you navigated to dashboard using a URL with an edit=true parameter and you did not have permission to edit it, although you were not in edit mode the side pane would incorrectly not appear.
SLAnalytics: Problem when stopping SLAnalytics features [ID 32734]
In some cases, an error could occur in the SLAnalytics process when SLAnalytics features were stopped.
SLAnalytics: Problem when checking the status of the Elasticsearch database [ID 32753]
In some cases, an error could occur in the SLAnalytics process when checking the status of the Elasticsearch database.
From now on, when SLAnalytics is unable to check the status of the Elasticsearch database, it will assume that database is inactive and will disable all SLAnalytics features that require an active Elasticsearch database.
Alarms and information events not migrated during migration to Cassandra Cluster [ID 32755]
When a DataMiner cluster with multiple DMAs was migrated to a Cassandra Cluster database, it could occur that the migration of alarms and information events failed because the DMAs tried to truncate the same table at the same time. Truncation will now take place in the initialization phase to prevent this problem, and if it fails, this will be logged but will not stop the migration. This will also prevent a rare problem where data could be missing after DMAs were migrated one by one.
DataMiner Cube - Asset Manager: UI could become unresponsive when the database configuration was being retrieved [ID 32766]
When, in DataMiner Cube, you opened the Asset Manager app, in some cases, the UI could become unresponsive when the database configuration was being retrieved.
SLAnalytics: Unneeded error was thrown when an upgrade action tried to remove the pattern match occurrences table from a non-existing Elasticsearch database [ID 32772]
On systems without an Elasticsearch database, the following messages were thrown when an upgrade action tried to remove the pattern match occurrences table from the non-existing Elasticsearch database:
10.102.0.12|2022-03-03 09:33:57|information|Elastic was not detected in DB.xml. Will not remove obsolete Elastic indices.
10.102.0.12|2022-03-03 09:33:58|error|Couldn't remove Elastic indices. Cause: Object reference not set to an instance of an object.
From now on, when no Elasticsearch database can be found, only the above-mentioned information event will be thrown.
Problems with embedded dashboards components [ID 32782]
When a GQI component was embedded in a Visio drawing or a web page, in some cases, that component would not be rendered correctly. Also, in some cases, embedded dashboard components would not be able to retrieve data from the database.
SLDataGateway: Result set would incorrectly be kept in memory after retrieving alarms from the database [ID 32788]
When alarms had been retrieved from the database page by page, in some cases, those pages would be kept in memory indefinitely.
SLAnalytics - Pattern matching: Disabling the monitoring of a pattern would not be applied immediately [ID 32792]
When you disabled the monitoring of a pattern that had monitoring enabled, the update would incorrectly only be applied after restarting either SLAnalytics or the DataMiner software.