Relational anomaly detection
From DataMiner 10.5.3/10.6.0 onwards, you can use relational anomaly detection (RAD) to detect when a group of parameters deviates from its normal behavior.
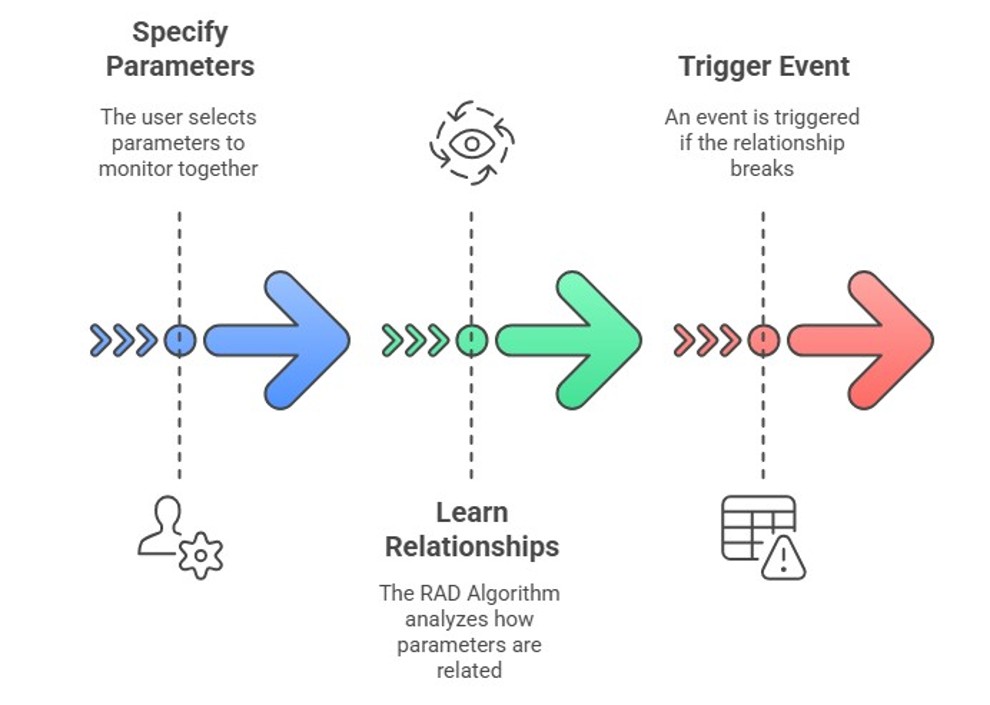
The RAD functionality works in three different steps:
First you need to configure one or more groups of parameters that should be monitored together, e.g. a main bit rate and backup bit rate.
The algorithm will then learn the relations between the parameters, e.g. learn that main and backup are typically equal. This is done automatically by the system, but you can manually specify a training range.
Whenever a detected relation is broken, e.g. the main is no longer equal to the backup, RAD will generate suggestion events in the Alarm Console.
Every five minutes, RAD calculates an anomaly score for each configured group of parameters. This score is based on the average value of each parameter in that group over the last five minutes. A high anomaly score indicates that the relationships between the parameters are broken, whereas a low anomaly score means the relationships remain intact. Historical anomaly scores can be visualized in the RAD Manager app.
Prerequisites
RAD uses average trending to detect anomalies. As such, it requires numeric parameters with at least one week of five-minute average trend data. If at least one parameter has less than a week of trend data available, monitoring will only start after one week of data has been collected.
This means that the following prerequisites apply:
- Average trending has to be enabled for each parameter used in a RAD group.
- The TTL for five-minute average trend data has to be set to more than one week (recommended setting: 1 month).
Use cases
By way of example, here are a few of the possible use cases for relational anomaly detection:
Main and backup transcoders (Xcoders): Monitor the output bit rate differences between main and backup transcoders to make sure that your backup remains synced with the main.
Bonded Interfaces: Spot differences in bit rates across bonded interfaces. This can provide early warnings for failures in the load balancing circuit or for issues with individual interfaces or fibers.
UPS Management: Decide on the best time to replace your battery. For a full use case description, refer to UPS Management Use Case.
Temperatures vs. fan speeds: Monitor whether the fan speed of a device is in sync with the temperature of the device. This can help identify faults in the cooling system or in the device itself.
Power amplifiers in DAB transmitters: Monitor the power outputs of all amplifiers in a DAB transmitter to ensure they remain in sync. This helps identify faults in the transmitter or the antenna system. For a tutorial on how to set up RAD for this use case, refer to Working with relational anomaly detection.
Configuring parameter groups for RAD
RAD only monitors parameters that have been added to one or more parameter groups in its configuration. Each parameter group represents a set of parameters that should be monitored together. RAD will learn how these parameters are related and notify you through a suggestion event when the relationship is broken.
The easiest way to configure these parameter groups is by using the RAD Manager app from the DataMiner Catalog. Alternatively, you can use the RAD API or directly configure the parameter groups in the RAD configuration XML file.
Options for parameter groups
For each parameter group, several configuration options are available. The table below provides an overview of these options:
Name in RAD Manager app |
Name in API and XML | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Group name | name |
The name of the parameter group. This name is used when generating a suggestion event or displaying all groups in the RAD Manager. |
| Update model on new data? | updateModel |
Indicates whether RAD should update its internal model of the relationships between the parameters in the group when new trend data is available. If this is not selected, the model will only be trained immediately after creation and when manually specifying a training range. Enabling this can be useful when monitoring parameters that you would like to see changing over time; the model can then adapt to the new behavior, and only more pronounced breaks in relations will be detected. If the parameter relationship is static (e.g. two parameters that should remain equal forever), it is better not to enable this option. |
| Anomaly threshold | anomalyThreshold in API, anomalyScore in XML |
The threshold used for suggestion event generation. Suggestion events are generated when RAD detects a region with an anomaly score higher than this threshold. A higher threshold results in fewer suggestion events, while a lower threshold results in more. Default: 3 |
| Minimum anomaly duration | minimumAnomalyDuration |
Supported from DataMiner 10.5.4/10.6.0 onwards. This option specifies the minimum duration (in minutes) that deviating behavior must persist to be considered a significant anomaly, similar to alarm hysteresis. This value must be 5 minutes or higher. If this is set to a value greater than 5 minutes, the deviating behavior must persist longer before an anomaly event is triggered. You can configure this to filter out noise events due to a single, short, harmless outlier, for instance caused by a planned maintenance or a device restart. Default: 5 minutes. |
Relational anomalies in the Alarm Console
Whenever the relationship for a parameter group is broken, RAD detects this and generates suggestion events in the Alarm Console. These events can be viewed in the Relational Anomalies tab, accessible through the Alarm Console light bulb, or in the Suggestion events tab (see Adding and Removing Alarm Tabs in the Alarm Console).
Suggestion events for the same group of parameters are grouped into a single incident. Clearing the grouped incident will also clear all suggestion events included in it. Other changes (e.g., taking ownership, adding comments) are not supported for grouped incidents. Note that prior to DataMiner 10.5.4, a separate suggestion event was generated for each parameter in the group where a broken relationship was detected.
From DataMiner 10.5.6/10.6.0 onwards, deleting a parameter group will also clear all open suggestion events associated with that group.
Limitations
RAD is only able to monitor parameters on the local DataMiner Agent. This means that all parameter instances configured in the RelationalAnomalyDetection.xml configuration file on a given DMA must be hosted on that same DMA. Currently, RAD is not able to simultaneously monitor parameters hosted on different DMAs.
Some parameter behavior will cause RAD to work less accurately. For example, if a parameter responds to another parameter with a delay, such as a door opening gradually lowering a room's temperature, RAD may generate less precise results.
Parameters on DVE children cannot be monitored directly by RAD. Instead, you should monitor the corresponding parameter instance on the DVE parent.
Relational anomalies on history set parameters can only be detected from DataMiner 10.5.4/10.6.0 onwards, and only under certain conditions:
- If there is at least one history set parameter in a RAD parameter group, that parameter group will only be processed when all data from all parameters in the group has been received. In other words, if a history set parameter receives data 30 minutes later than the real-time parameters, possible anomalies will only be detected after 30 minutes.
- RAD will only process data received within the last hour. If a history set parameter receives data more than an hour later than the real-time parameters, that data will be disregarded.