Resource Studio
The Resource Studio app serves as a comprehensive platform for creating and managing resources. Its key features include the ability to create diverse resources, ranging from network inventory to services and other limited-availability items such as rooms, people, vehicles etc. Users can organize these resources into pools, simplifying workflow and job resource selection. Capabilities and capacities can be assigned to resources, facilitating precise resource allocation based on specific job requirements. Users can also store supplementary information as properties, enhancing the resource management process.
Tip
Do you prefer visual learning? Take a look at the demo video about this app.
App overview
The following pages are available in the app:
 Resource Pools: Allows you to create, edit, delete, search, and filter resource pools. You can also assign resources to resource pools, and edit capabilities, capacities, and properties for each resource pool.
Resource Pools: Allows you to create, edit, delete, search, and filter resource pools. You can also assign resources to resource pools, and edit capabilities, capacities, and properties for each resource pool. Resources: Allows you to create and manage specific resources, and configure their capabilities, capacities, and properties.
Resources: Allows you to create and manage specific resources, and configure their capabilities, capacities, and properties. Capability Management: Here you can create and manage capabilities, and assign the possible values they can have when associated with resources and resource pools.
Capability Management: Here you can create and manage capabilities, and assign the possible values they can have when associated with resources and resource pools. Capacity Management: Here you can create and manage capacities.
Capacity Management: Here you can create and manage capacities. Configuration Management: If a resource pool has parameters that can be defined per job in the Scheduling app, you can add those types of parameters here. You can give the configurations default values or make it mandatory to configure them upon job creation.
Configuration Management: If a resource pool has parameters that can be defined per job in the Scheduling app, you can add those types of parameters here. You can give the configurations default values or make it mandatory to configure them upon job creation. Properties: Allows you to manage properties that can be used by resources and resource pools.
Properties: Allows you to manage properties that can be used by resources and resource pools. Sync: Allows you to sync the resources from DataMiner Cube with the resource representations used in MediaOps. If you choose to sync them, before any changes are made, you will get a message specifying each change that will take place. After the sync, MediaOps resources will be updated to mirror the DataMiner resources.
Sync: Allows you to sync the resources from DataMiner Cube with the resource representations used in MediaOps. If you choose to sync them, before any changes are made, you will get a message specifying each change that will take place. After the sync, MediaOps resources will be updated to mirror the DataMiner resources. About: Provides information on the version of the MediaOps package.
About: Provides information on the version of the MediaOps package.
Resources
The Resource Studio app allows you to create and manage resources. A resource can represent anything that involves managed use over time. Some examples of things a resource can represent include:
A piece of network inventory managed by DataMiner, such as an IRD, a cloud-based encoder, or a port on a switch.
An entire service managed by DataMiner that can be made available for use, such as an uplink connection with a certain bandwidth that will be available for a certain period of time.
Anything with limited availability that is not managed by DataMiner, such as rooms, people, vehicles, satellite transponder slots, IP addresses, etc.
Each resource has a concurrency setting, which defines how many bookings of the resource can be made at the same time. By default, this is set to 1.
Resource pools
A resource pool can be created to group a set of interchangeable resources. This allows users who utilize resources in other apps to refer to a pool instead of a specific resource. This makes it possible to defer resource selection until the resource is actually needed, instead of assigning a specific resource at booking creation.
Resources can be added to multiple pools, making them eligible for multiple purposes while keeping a single availability timeline and preventing resource conflicts.
The resource pools displayed in the app include teams that have been made bookable in the People & Organizations app. These resource pools cannot be edited directly in the Resource Studio app.
Tip
For a detailed example of how you can add resource pools and resources, refer to the tutorial Configuring resources and resource pools.
Capabilities
Capabilities give a qualitative description of a resource or pool, making it clear what it can be used for.

Each capability has a name and a list of values. Users can assign one or more values to a resource or a pool. Examples of capabilities include:
Encoding: H.264, JPEG XS, JPEG 2K, etc.
Video Format: SD, HD, UHD
Modulation type: DVB-S, NS3, NS4
Capabilities can be assigned either to a resource or to a resource pool. If they are assigned to a resource pool, all resources in that pool will inherit the capabilities of the pool, but extra capabilities can also be added to individual resources. For example, in the screenshot above, you can see that the Decoding options are inherited from the pool, as the pool icon is displayed next to them.
When creating a workflow or a job, users can specify the required capabilities of the resources to be used in the workflow or job. This will limit the resources available for picking only to those which satisfy the capability requirements, making it easier to find the suitable ones.
For example, Location can be an important capability when planning operations where resources need to be on-site. You can assign locations to all your resources beforehand, and then upon job creation you can choose the location your resources need to have. Then, when the resources are picked, only the ones on the actual location will be available for selection. Capabilities offer a very flexible and general way of solving this problem for a wide array of cases.
In case a resource can be used multiple times (concurrency > 1), it could be that it can have multiple possible values, but only one value can be used at a given time. This could for example be a steerable antenna that can point to only one satellite at a time. For this, time-dependent capabilities can be used. This allows you to configure the resource with multiple possible values, but when the resource is booked with a specific value, all overlapping jobs using the same resource will have to have the same value in order to select the same resource.
Tip
For hands-on examples of using resources and resource pools with capabilities, you can follow several tutorials:
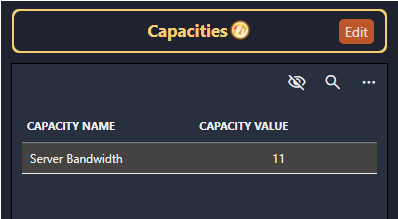
Capacities
Capacities, like capabilities, define how a resource can be used, but they are measured numerically. The following settings can be configured for capacities:
Units: The unit for the values of this capacity (MHz, Gbps, kBd, etc.).
Min. range: The minimum value allowed for this capacity.
Max. range: The maximum value allowed for this capacity.
Step size: The increment that can be used to change the capacity's values.
Decimals: The number of decimals allowed for values of this capacity.
Typical examples of capacities are bandwidths, bit rates, symbol rates, etc. When booking a resource, users book only a specific amount of capacity on the resource. If a resource has a concurrency higher than one, other jobs can still make use of the remaining capacity on that same resource.
Contrary to capabilities, capacities cannot be configured on resource pools, but only on individual resources.
However, similar to capabilities, capacities can also be used when creating jobs and workflows. You can specify capabilities on your resources, and then limit the resources available for picking in jobs and workflows based on those constraints.
Properties
Properties store extra details that do not affect resource selection.
Some examples of properties include data such as:
Contact person
Vendor name
Geolocation